Motion Planning
The Motion Planning Plugin
MoveIt works with motion planners through a plugin interface.
This allows MoveIt to communicate with and use different motion planners from multiple libraries, making MoveIt easily extensible. The interface to the motion planners is through a ROS action or service (offered by the move_group node).
The default motion planners for move_group are configured using OMPL and the MoveIt interface to OMPL by the MoveIt Setup Assistant.
Other planners that are available by default are the Pilz industrial motion planner and CHOMP.
The Motion Plan Request
The motion plan request specifies what you would like the motion planner to do.
Typically, you will be asking the motion planner to move an arm to a different location (in joint space) or the end-effector to a new pose.
Collisions are checked for by default (including self-collisions and attached objects).
You can also specify the planner via the planning_pipeline and planner_id parameters, and the constraints for the motion planner to check - the inbuilt constraints provided by MoveIt are kinematic constraints:
Position constraints: restrict the position of a link to lie within a region of space.
Orientation constraints: restrict the orientation of a link to lie within specified roll, pitch or yaw limits.
Visibility constraints: restrict a point on a link to lie within the visibility cone for a particular sensor.
Joint constraints: restrict a joint to lie between two values.
User-specified constraints: it is also possible to specify your own constraints with a user-defined callback.
The Motion Plan Result
The move_group node will generate a desired trajectory in response to your motion plan request. This trajectory will move the arm (or any group of joints) to the desired location. Note that the result coming out of move_group is a trajectory and not just a path. move_group will use the desired maximum velocities and accelerations (if specified) to generate a trajectory that obeys velocity and acceleration constraints at the joint level.
Motion planning adapters
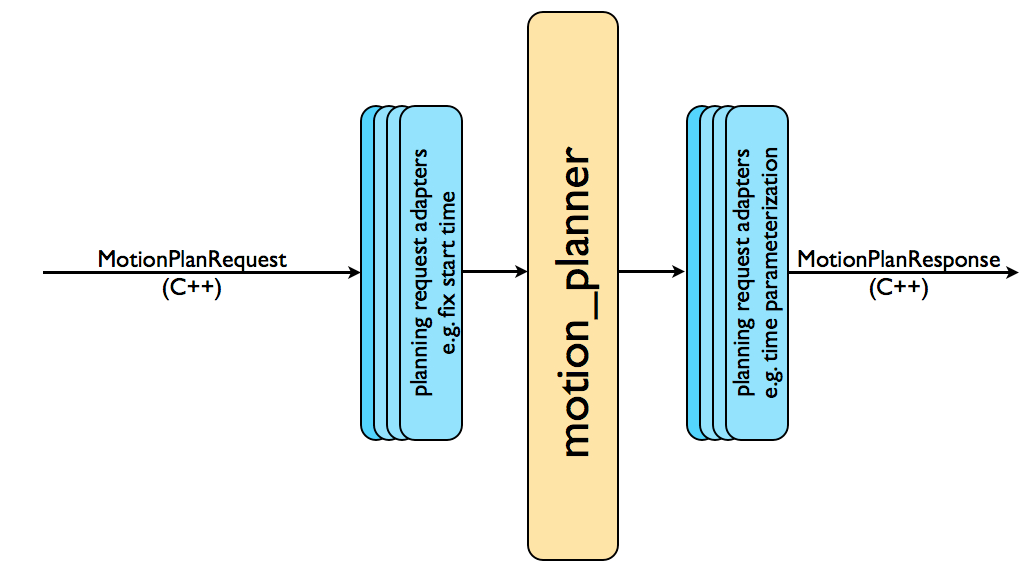
The complete motion planning pipeline chains together a motion planner with other components called planning request adapters. Planning request adapters allow for pre-processing motion plan requests and post-processing motion plan responses. Pre-processing is useful in several situations, e.g. when a start state for the robot is slightly outside the specified joint limits for the robot. Post-processing is needed for several other operations, e.g. to convert paths generated for a robot into time-parameterized trajectories. MoveIt provides a set of default motion planning adapters that each perform a very specific function.
CheckStartStateBounds
The fix start state bounds adapter fixes the start state to be within the joint limits specified in the URDF. The need for this adapter arises in situations where the joint limits for the physical robot are not properly configured. The robot may then end up in a configuration where one or more of its joints is slightly outside its joint limits. In this case, the motion planner is unable to plan since it will think that the starting state is outside joint limits. The “CheckStartStateBounds” planning request adapter will “fix” the start state by moving it to the joint limit. However, this is obviously not the right solution every time - e.g. where the joint is really outside its joint limits by a large amount. A parameter for the adapter specifies how much the joint can be outside its limits for it to be “fixable”.
ValidateWorkspaceBounds
The fix workspace bounds adapter will specify a default workspace for planning: a cube of size 10 m x 10 m x 10 m. This workspace will only be specified if the planning request to the planner does not have these fields filled in.
CheckStartStateCollision
The fix start state collision adapter will attempt to sample a new collision-free configuration near a specified configuration (in collision) by perturbing the joint values by a small amount. The amount that it will perturb the values by is specified by the jiggle_fraction parameter that controls the perturbation as a percentage of the total range of motion for the joint. The other parameter for this adapter specifies how many random perturbations the adapter will sample before giving up.
AddTimeParameterization
The motion planners will typically generate “kinematic paths”, i.e., paths that do not obey any velocity or acceleration constraints and are not time parameterized. This adapter will “time parameterize” the motion plans by applying velocity and acceleration constraints.
ResolveConstraintFrames
Goal constraints can be set using subframes (e.g. a pose goal in the frame cup/handle, where handle is a subframe on the object cup).
This adapter changes the frame of constraints to an object or robot frame (e.g. cup).
OMPL
OMPL (Open Motion Planning Library) is an open-source motion planning library that primarily implements randomized motion planners. MoveIt integrates directly with OMPL and uses the motion planners from that library as its primary/default set of planners. The planners in OMPL are abstract; i.e. OMPL has no concept of a robot. Instead, MoveIt configures OMPL and provides the back-end for OMPL to work with problems in Robotics.