Parallel Containers
Parallel containers combine a set of stages to allow planning alternate solutions.
Three stages provided by MTC to use within a parallel container:
AlternativesFallbackMerger
Alternatives
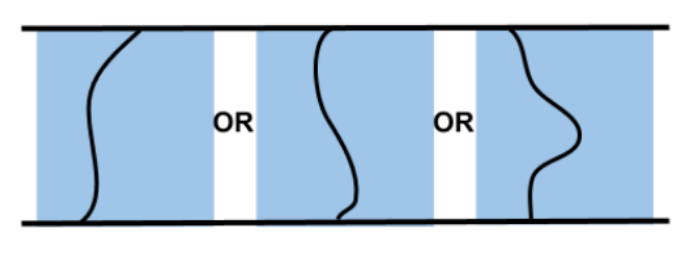
Alternatives containers allow adding stages to be executed in parallel.
All the solutions of the child stages are collected at the end and ordered by cost.
Example - Plan a trajectory with multiple cost terms.
auto pipeline{ std::make_shared<solvers::PipelinePlanner>(node) };
auto alternatives{ std::make_unique<Alternatives>("connect") };
{
auto connect{ std::make_unique<stages::Connect>(
"path length", stages::Connect::GroupPlannerVector{ { "panda_arm", pipeline } }) };
connect->setCostTerm(std::make_unique<cost::PathLength>());
alternatives->add(std::move(connect));
}
{
auto connect{ std::make_unique<stages::Connect>(
"trajectory duration", stages::Connect::GroupPlannerVector{ { "panda_arm", pipeline } }) };
connect->setCostTerm(std::make_unique<cost::TrajectoryDuration>());
alternatives->add(std::move(connect));
}
t.add(std::move(alternatives));
Fallbacks
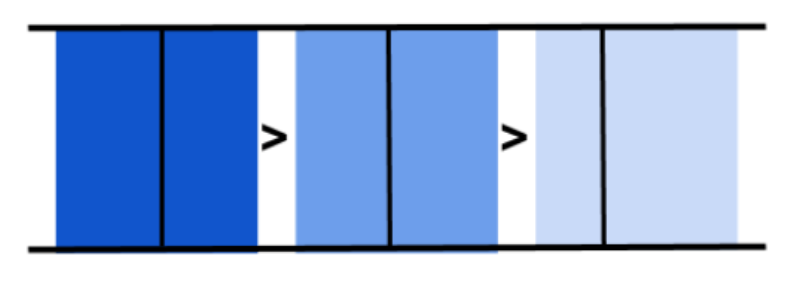
A fallback container executes child stages in order until one of them returns success or all stages return failure.
Example - Plan with different solvers one at a time until we get a successful solution.
auto cartesian = std::make_shared<solvers::CartesianPath>();
auto ptp = std::make_shared<solvers::PipelinePlanner>(node, "pilz_industrial_motion_planner", "PTP")
auto rrtconnect = std::make_shared<solvers::PipelinePlanner>(node, "ompl", "RRTConnectkConfigDefault")
// fallbacks to reach target_state
auto fallbacks = std::make_unique<Fallbacks>("move to other side");
auto add_to_fallbacks{ [&](auto& solver, auto& name) {
auto move_to = std::make_unique<stages::MoveTo>(name, solver);
move_to->setGroup("panda_arm");
move_to->setGoal(target_state);
fallbacks->add(std::move(move_to));
} };
add_to_fallbacks(cartesian, "Cartesian path");
add_to_fallbacks(ptp, "PTP path");
add_to_fallbacks(rrtconnect, "RRT path");
Merger
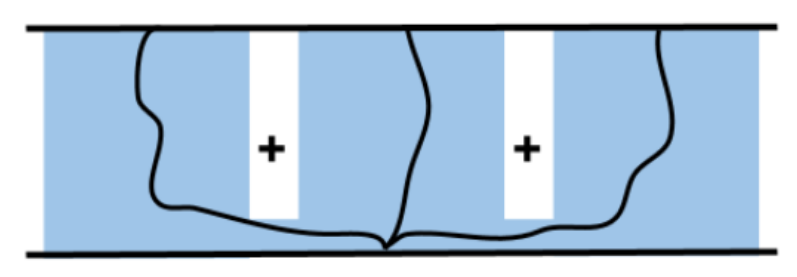
Stages in a Merger container combine multiple distinct problems, i.e., plan for different planning groups in parallel.
Solutions of all children are merged into a single solution for parallel execution.
Example - Open gripper while moving the arm to a location
auto cartesian_planner = std::make_shared<solvers::CartesianPath>();
const auto joint_interpolation_planner = std::make_shared<moveit::task_constructor::solvers::JointInterpolationPlanner>();
auto merger = std::make_unique<Merger>("move arm and close gripper");
auto move_relative = std::make_unique<moveit::task_constructor::stages::MoveRelative>("Approach", cartesian_planner);
merger->add(std::move(move_relative));
auto move_to =
std::make_unique<moveit::task_constructor::stages::MoveTo>("close gripper", joint_interpolation_planner);
merger->add(std::move(move_to));