Representation of a robot's state. This includes position, velocity, acceleration and effort. More...
#include <robot_state.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| RobotState (const RobotModelConstPtr &robot_model) | |
| A state can be constructed from a specified robot model. No values are initialized. Call setToDefaultValues() if a state needs to provide valid information. More... | |
| ~RobotState () | |
| RobotState (const RobotState &other) | |
| Copy constructor. More... | |
| RobotState & | operator= (const RobotState &other) |
| Copy operator. More... | |
| const RobotModelConstPtr & | getRobotModel () const |
| Get the robot model this state is constructed for. More... | |
| std::size_t | getVariableCount () const |
| Get the number of variables that make up this state. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getVariableNames () const |
| Get the names of the variables that make up this state, in the order they are stored in memory. More... | |
| const LinkModel * | getLinkModel (const std::string &link) const |
| Get the model of a particular link. More... | |
| const JointModel * | getJointModel (const std::string &joint) const |
| Get the model of a particular joint. More... | |
| const JointModelGroup * | getJointModelGroup (const std::string &group) const |
| Get the model of a particular joint group. More... | |
| void | computeAABB (std::vector< double > &aabb) const |
| Compute an axis-aligned bounding box that contains the current state. The format for aabb is (minx, maxx, miny, maxy, minz, maxz) More... | |
| void | computeAABB (std::vector< double > &aabb) |
| Compute an axis-aligned bounding box that contains the current state. The format for aabb is (minx, maxx, miny, maxy, minz, maxz) More... | |
| random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator & | getRandomNumberGenerator () |
| Return the instance of a random number generator. More... | |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getFrameTransform (const std::string &frame_id, bool *frame_found=nullptr) |
| Get the transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to the frame identified by frame_id. More... | |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getFrameTransform (const std::string &frame_id, bool *frame_found=nullptr) const |
| Get the transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to the frame identified by frame_id. More... | |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getFrameInfo (const std::string &frame_id, const LinkModel *&robot_link, bool &frame_found) const |
| Get the transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to the frame identified by frame_id. More... | |
| bool | knowsFrameTransform (const std::string &frame_id) const |
| Check if a transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to frame frame_id is known. More... | |
| void | getRobotMarkers (visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray &arr, const std::vector< std::string > &link_names, const std_msgs::msg::ColorRGBA &color, const std::string &ns, const rclcpp::Duration &dur, bool include_attached=false) const |
| Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot. More... | |
| void | getRobotMarkers (visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray &arr, const std::vector< std::string > &link_names, const std_msgs::msg::ColorRGBA &color, const std::string &ns, const rclcpp::Duration &dur, bool include_attached=false) |
| Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot. Update the state first. More... | |
| void | getRobotMarkers (visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray &arr, const std::vector< std::string > &link_names, bool include_attached=false) const |
| Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot. More... | |
| void | getRobotMarkers (visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray &arr, const std::vector< std::string > &link_names, bool include_attached=false) |
| Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot. Update the state first. More... | |
| void | printStatePositions (std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| void | printStatePositionsWithJointLimits (const moveit::core::JointModelGroup *jmg, std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| Output to console the current state of the robot's joint limits. More... | |
| void | printStateInfo (std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| void | printTransforms (std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| void | printTransform (const Eigen::Isometry3d &transform, std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| void | printDirtyInfo (std::ostream &out=std::cout) const |
| std::string | getStateTreeString () const |
| bool | setToIKSolverFrame (Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, const kinematics::KinematicsBaseConstPtr &solver) |
| Transform pose from the robot model's base frame to the reference frame of the IK solver. More... | |
| bool | setToIKSolverFrame (Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, const std::string &ik_frame) |
| Transform pose from the robot model's base frame to the reference frame of the IK solver. More... | |
Getting and setting variable position | |
| double * | getVariablePositions () |
| Get a raw pointer to the positions of the variables stored in this state. Use carefully. If you change these values externally you need to make sure you trigger a forced update for the state by calling update(true). More... | |
| const double * | getVariablePositions () const |
| Get a raw pointer to the positions of the variables stored in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariablePositions (const double *position) |
| It is assumed positions is an array containing the new positions for all variables in this state. Those values are copied into the state. More... | |
| void | setVariablePositions (const std::vector< double > &position) |
| It is assumed positions is an array containing the new positions for all variables in this state. Those values are copied into the state. More... | |
| void | setVariablePositions (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map) |
| Set the positions of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariablePositions (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map, std::vector< std::string > &missing_variables) |
| Set the positions of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set. More... | |
| void | setVariablePositions (const std::vector< std::string > &variable_names, const std::vector< double > &variable_position) |
| Set the positions of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set. More... | |
| void | setVariablePosition (const std::string &variable, double value) |
| Set the position of a single variable. An exception is thrown if the variable name is not known. More... | |
| void | setVariablePosition (int index, double value) |
| Set the position of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable) More... | |
| double | getVariablePosition (const std::string &variable) const |
| Get the position of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known. More... | |
| double | getVariablePosition (int index) const |
| Get the position of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed More... | |
Getting and setting variable velocity | |
| bool | hasVelocities () const |
| By default, if velocities are never set or initialized, the state remembers that there are no velocities set. This is useful to know when serializing or copying the state. More... | |
| double * | getVariableVelocities () |
| Get raw access to the velocities of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames() More... | |
| const double * | getVariableVelocities () const |
| Get const access to the velocities of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames() More... | |
| void | zeroVelocities () |
| Set all velocities to 0.0. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocities (const double *velocity) |
| Given an array with velocity values for all variables, set those values as the velocities in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocities (const std::vector< double > &velocity) |
| Given an array with velocity values for all variables, set those values as the velocities in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocities (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map) |
| Set the velocities of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocities (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map, std::vector< std::string > &missing_variables) |
| Set the velocities of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocities (const std::vector< std::string > &variable_names, const std::vector< double > &variable_velocity) |
| Set the velocities of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocity (const std::string &variable, double value) |
| Set the velocity of a variable. If an unknown variable name is specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableVelocity (int index, double value) |
| Set the velocity of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable) More... | |
| double | getVariableVelocity (const std::string &variable) const |
| Get the velocity of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known. More... | |
| double | getVariableVelocity (int index) const |
| Get the velocity of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed More... | |
| void | dropVelocities () |
| Remove velocities from this state (this differs from setting them to zero) More... | |
Getting and setting variable acceleration | |
| bool | hasAccelerations () const |
| By default, if accelerations are never set or initialized, the state remembers that there are no accelerations set. This is useful to know when serializing or copying the state. If hasAccelerations() reports true, hasEffort() will certainly report false. More... | |
| double * | getVariableAccelerations () |
| Get raw access to the accelerations of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames(). The area of memory overlaps with effort (effort and acceleration should not be set at the same time) More... | |
| const double * | getVariableAccelerations () const |
| Get const raw access to the accelerations of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames() More... | |
| void | zeroAccelerations () |
| Set all accelerations to 0.0. More... | |
| void | setVariableAccelerations (const double *acceleration) |
| Given an array with acceleration values for all variables, set those values as the accelerations in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariableAccelerations (const std::vector< double > &acceleration) |
| Given an array with acceleration values for all variables, set those values as the accelerations in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariableAccelerations (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map) |
| Set the accelerations of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableAccelerations (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map, std::vector< std::string > &missing_variables) |
| Set the accelerations of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set. More... | |
| void | setVariableAccelerations (const std::vector< std::string > &variable_names, const std::vector< double > &variable_acceleration) |
| Set the accelerations of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableAcceleration (const std::string &variable, double value) |
| Set the acceleration of a variable. If an unknown variable name is specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableAcceleration (int index, double value) |
| Set the acceleration of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable) More... | |
| double | getVariableAcceleration (const std::string &variable) const |
| Get the acceleration of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known. More... | |
| double | getVariableAcceleration (int index) const |
| Get the acceleration of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed More... | |
| void | dropAccelerations () |
| Remove accelerations from this state (this differs from setting them to zero) More... | |
Getting and setting variable effort | |
| bool | hasEffort () const |
| By default, if effort is never set or initialized, the state remembers that there is no effort set. This is useful to know when serializing or copying the state. If hasEffort() reports true, hasAccelerations() will certainly report false. More... | |
| double * | getVariableEffort () |
| Get raw access to the effort of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames(). The area of memory overlaps with accelerations (effort and acceleration should not be set at the same time) More... | |
| const double * | getVariableEffort () const |
| Get const raw access to the effort of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames(). More... | |
| void | zeroEffort () |
| Set all effort values to 0.0. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (const double *effort) |
| Given an array with effort values for all variables, set those values as the effort in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (const std::vector< double > &effort) |
| Given an array with effort values for all variables, set those values as the effort in this state. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map) |
| Set the effort of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_map, std::vector< std::string > &missing_variables) |
| Set the effort of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (const std::vector< std::string > &variable_names, const std::vector< double > &variable_acceleration) |
| Set the effort of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (const std::string &variable, double value) |
| Set the effort of a variable. If an unknown variable name is specified, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | setVariableEffort (int index, double value) |
| Set the effort of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable) More... | |
| double | getVariableEffort (const std::string &variable) const |
| Get the effort of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known. More... | |
| double | getVariableEffort (int index) const |
| Get the effort of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed More... | |
| void | dropEffort () |
| Remove effort values from this state (this differs from setting them to zero) More... | |
| void | dropDynamics () |
| Reduce RobotState to kinematic information (remove velocity, acceleration and effort, if present) More... | |
| void | invertVelocity () |
| Invert velocity if present. More... | |
Getting and setting joint positions, velocities, accelerations and effort for a single joint | |
The joint might be multi-DOF, i.e. require more than one variable to set. See setVariablePositions(), setVariableVelocities(), setVariableEffort() to handle multiple joints. | |
| void | setJointPositions (const std::string &joint_name, const double *position) |
| void | setJointPositions (const std::string &joint_name, const std::vector< double > &position) |
| void | setJointPositions (const JointModel *joint, const std::vector< double > &position) |
| void | setJointPositions (const JointModel *joint, const double *position) |
| void | setJointPositions (const std::string &joint_name, const Eigen::Isometry3d &transform) |
| void | setJointPositions (const JointModel *joint, const Eigen::Isometry3d &transform) |
| void | setJointVelocities (const JointModel *joint, const double *velocity) |
| void | setJointEfforts (const JointModel *joint, const double *effort) |
| const double * | getJointPositions (const std::string &joint_name) const |
| const double * | getJointPositions (const JointModel *joint) const |
| const double * | getJointVelocities (const std::string &joint_name) const |
| const double * | getJointVelocities (const JointModel *joint) const |
| const double * | getJointAccelerations (const std::string &joint_name) const |
| const double * | getJointAccelerations (const JointModel *joint) const |
| const double * | getJointEffort (const std::string &joint_name) const |
| const double * | getJointEffort (const JointModel *joint) const |
Getting and setting group positions | |
| void | setJointGroupPositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, const double *gstate) |
| Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupPositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, const double *gstate) |
| Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupPositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupActivePositions (const JointModelGroup *group, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupActivePositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupActivePositions (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupActivePositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupPositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, std::vector< double > &gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupPositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, double *gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, std::vector< double > &gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, double *gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupPositions (const std::string &joint_group_name, Eigen::VectorXd &values) const |
| For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, Eigen::VectorXd &values) const |
| For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
Getting and setting group velocities | |
| void | setJointGroupVelocities (const std::string &joint_group_name, const double *gstate) |
| Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupVelocities (const std::string &joint_group_name, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupVelocities (const JointModelGroup *group, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupVelocities (const JointModelGroup *group, const double *gstate) |
| Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupVelocities (const std::string &joint_group_name, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupVelocities (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupVelocities (const std::string &joint_group_name, std::vector< double > &gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupVelocities (const std::string &joint_group_name, double *gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupVelocities (const JointModelGroup *group, std::vector< double > &gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupVelocities (const JointModelGroup *group, double *gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupVelocities (const std::string &joint_group_name, Eigen::VectorXd &values) const |
| For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupVelocities (const JointModelGroup *group, Eigen::VectorXd &values) const |
| For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
Getting and setting group accelerations | |
| void | setJointGroupAccelerations (const std::string &joint_group_name, const double *gstate) |
| Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupAccelerations (const std::string &joint_group_name, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupAccelerations (const JointModelGroup *group, const std::vector< double > &gstate) |
| Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupAccelerations (const JointModelGroup *group, const double *gstate) |
| Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupAccelerations (const std::string &joint_group_name, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | setJointGroupAccelerations (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::VectorXd &values) |
| Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupAccelerations (const std::string &joint_group_name, std::vector< double > &gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupAccelerations (const std::string &joint_group_name, double *gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupAccelerations (const JointModelGroup *group, std::vector< double > &gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupAccelerations (const JointModelGroup *group, double *gstate) const |
| For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupAccelerations (const std::string &joint_group_name, Eigen::VectorXd &values) const |
| For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
| void | copyJointGroupAccelerations (const JointModelGroup *group, Eigen::VectorXd &values) const |
| For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer. More... | |
Setting from Inverse Kinematics | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose &pose, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose &pose, const std::string &tip, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, const std::string &tip, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, const std::string &tip, const std::vector< double > &consistency_limits, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &poses, const std::vector< std::string > &tips, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| Warning: This function inefficiently copies all transforms around. If the group consists of a set of sub-groups that are each a chain and a solver is available for each sub-group, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The poses are assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. The poses are assumed to be in the same order as the order of the sub-groups in this group. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &poses, const std::vector< std::string > &tips, const std::vector< std::vector< double >> &consistency_limits, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn &cost_function=kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn()) |
| Warning: This function inefficiently copies all transforms around. If the group consists of a set of sub-groups that are each a chain and a solver is available for each sub-group, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The poses are assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. The poses are assumed to be in the same order as the order of the sub-groups in this group. Returns true on success. More... | |
| bool | setFromIKSubgroups (const JointModelGroup *group, const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &poses, const std::vector< std::string > &tips, const std::vector< std::vector< double >> &consistency_limits, double timeout=0.0, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions()) |
| setFromIK for multiple poses and tips (end effectors) when no solver exists for the jmg that can solver for non-chain kinematics. In this case, we divide the group into subgroups and do IK solving individually More... | |
| bool | setFromDiffIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::VectorXd &twist, const std::string &tip, double dt, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn()) |
| Set the joint values from a Cartesian velocity applied during a time dt. More... | |
| bool | setFromDiffIK (const JointModelGroup *group, const geometry_msgs::msg::Twist &twist, const std::string &tip, double dt, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn()) |
| Set the joint values from a Cartesian velocity applied during a time dt. More... | |
| double | computeCartesianPath (const JointModelGroup *group, std::vector< RobotStatePtr > &traj, const LinkModel *link, const Eigen::Vector3d &direction, bool global_reference_frame, double distance, double max_step, double jump_threshold_factor, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &validCallback=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions()) |
| Compute the sequence of joint values that correspond to a straight Cartesian path for a particular group. More... | |
| double | computeCartesianPath (const JointModelGroup *group, std::vector< RobotStatePtr > &traj, const LinkModel *link, const Eigen::Isometry3d &target, bool global_reference_frame, double max_step, double jump_threshold_factor, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &validCallback=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions()) |
| Compute the sequence of joint values that correspond to a straight Cartesian path, for a particular group. More... | |
| double | computeCartesianPath (const JointModelGroup *group, std::vector< RobotStatePtr > &traj, const LinkModel *link, const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &waypoints, bool global_reference_frame, double max_step, double jump_threshold_factor, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &validCallback=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions &options=kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions()) |
| Compute the sequence of joint values that perform a general Cartesian path. More... | |
| bool | getJacobian (const JointModelGroup *group, const LinkModel *link, const Eigen::Vector3d &reference_point_position, Eigen::MatrixXd &jacobian, bool use_quaternion_representation=false) const |
| Compute the Jacobian with reference to a particular point on a given link, for a specified group. More... | |
| bool | getJacobian (const JointModelGroup *group, const LinkModel *link, const Eigen::Vector3d &reference_point_position, Eigen::MatrixXd &jacobian, bool use_quaternion_representation=false) |
| Compute the Jacobian with reference to a particular point on a given link, for a specified group. More... | |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | getJacobian (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::Vector3d &reference_point_position=Eigen::Vector3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) const |
| Compute the Jacobian with reference to the last link of a specified group. If the group is not a chain, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| Eigen::MatrixXd | getJacobian (const JointModelGroup *group, const Eigen::Vector3d &reference_point_position=Eigen::Vector3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) |
| Compute the Jacobian with reference to the last link of a specified group. If the group is not a chain, an exception is thrown. More... | |
| void | computeVariableVelocity (const JointModelGroup *jmg, Eigen::VectorXd &qdot, const Eigen::VectorXd &twist, const LinkModel *tip) const |
| Given a twist for a particular link (tip), compute the corresponding velocity for every variable and store it in qdot. More... | |
| void | computeVariableVelocity (const JointModelGroup *jmg, Eigen::VectorXd &qdot, const Eigen::VectorXd &twist, const LinkModel *tip) |
| Given a twist for a particular link (tip), compute the corresponding velocity for every variable and store it in qdot. More... | |
| bool | integrateVariableVelocity (const JointModelGroup *jmg, const Eigen::VectorXd &qdot, double dt, const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn &constraint=GroupStateValidityCallbackFn()) |
| Given the velocities for the variables in this group (qdot) and an amount of time (dt), update the current state using the Euler forward method. If the constraint specified is satisfied, return true, otherwise return false. More... | |
Getting and setting whole states | |
| void | setVariableValues (const sensor_msgs::msg::JointState &msg) |
| void | setToDefaultValues () |
| Set all joints to their default positions. The default position is 0, or if that is not within bounds then half way between min and max bound. More... | |
| bool | setToDefaultValues (const JointModelGroup *group, const std::string &name) |
| Set the joints in group to the position name defined in the SRDF. More... | |
| bool | setToDefaultValues (const std::string &group_name, const std::string &state_name) |
| void | setToRandomPositions () |
| Set all joints to random values. Values will be within default bounds. More... | |
| void | setToRandomPositions (const JointModelGroup *group) |
| Set all joints in group to random values. Values will be within default bounds. More... | |
| void | setToRandomPositions (const JointModelGroup *group, random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator &rng) |
| Set all joints in group to random values using a specified random number generator. Values will be within default bounds. More... | |
| void | setToRandomPositionsNearBy (const JointModelGroup *group, const RobotState &seed, double distance) |
| Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed. distance is the maximum amount each joint value will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds. More... | |
| void | setToRandomPositionsNearBy (const JointModelGroup *group, const RobotState &seed, double distance, random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator &rng) |
| Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed, using a specified random number generator. distance is the maximum amount each joint value will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds. More... | |
| void | setToRandomPositionsNearBy (const JointModelGroup *group, const RobotState &seed, const std::vector< double > &distances) |
Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed. distances MUST have the same size as group.getActiveJointModels(). Each value in distances is the maximum amount the corresponding active joint in group will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds. More... | |
| void | setToRandomPositionsNearBy (const JointModelGroup *group, const RobotState &seed, const std::vector< double > &distances, random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator &rng) |
Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed, using a specified random number generator. distances MUST have the same size as group.getActiveJointModels(). Each value in distances is the maximum amount the corresponding active joint in group will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds. More... | |
Updating and getting transforms | |
| void | updateCollisionBodyTransforms () |
| Update the transforms for the collision bodies. This call is needed before calling collision checking. If updating link transforms or joint transforms is needed, the corresponding updates are also triggered. More... | |
| void | updateLinkTransforms () |
| Update the reference frame transforms for links. This call is needed before using the transforms of links for coordinate transforms. More... | |
| void | update (bool force=false) |
| Update all transforms. More... | |
| void | updateStateWithLinkAt (const std::string &link_name, const Eigen::Isometry3d &transform, bool backward=false) |
| Update the state after setting a particular link to the input global transform pose. More... | |
| void | updateStateWithLinkAt (const LinkModel *link, const Eigen::Isometry3d &transform, bool backward=false) |
| Update the state after setting a particular link to the input global transform pose. More... | |
| const moveit::core::LinkModel * | getRigidlyConnectedParentLinkModel (const std::string &frame, const moveit::core::JointModelGroup *jmg=nullptr) const |
| Get the latest link upwards the kinematic tree which is only connected via fixed joints. More... | |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getGlobalLinkTransform (const std::string &link_name) |
| Get the link transform w.r.t. the root link (model frame) of the RobotModel. This is typically the root link of the URDF unless a virtual joint is present. Checks the cache and if there are any dirty (non-updated) transforms, first updates them as needed. A related, more comprehensive function is |getFrameTransform|, which additionally to link frames also searches for attached object frames and their subframes. More... | |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getGlobalLinkTransform (const LinkModel *link) |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getGlobalLinkTransform (const std::string &link_name) const |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getGlobalLinkTransform (const LinkModel *link) const |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getCollisionBodyTransform (const std::string &link_name, std::size_t index) |
| Get the link transform w.r.t. the root link (model frame) of the RobotModel. This is typically the root link of the URDF unless a virtual joint is present. Checks the cache and if there are any dirty (non-updated) transforms, first updates them as needed. More... | |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getCollisionBodyTransform (const LinkModel *link, std::size_t index) |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getCollisionBodyTransform (const std::string &link_name, std::size_t index) const |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getCollisionBodyTransform (const LinkModel *link, std::size_t index) const |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getJointTransform (const std::string &joint_name) |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getJointTransform (const JointModel *joint) |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getJointTransform (const std::string &joint_name) const |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | getJointTransform (const JointModel *joint) const |
| bool | dirtyJointTransform (const JointModel *joint) const |
| bool | dirtyLinkTransforms () const |
| bool | dirtyCollisionBodyTransforms () const |
| bool | dirty () const |
| Returns true if anything in this state is dirty. More... | |
Computing distances | |
| double | distance (const RobotState &other) const |
| Return the sum of joint distances to "other" state. An L1 norm. Only considers active joints. More... | |
| double | distance (const RobotState &other, const JointModelGroup *joint_group) const |
| Return the sum of joint distances to "other" state. An L1 norm. Only considers active joints. More... | |
| double | distance (const RobotState &other, const JointModel *joint) const |
| Return the sum of joint distances to "other" state. An L1 norm. Only considers active joints. More... | |
| void | interpolate (const RobotState &to, double t, RobotState &state) const |
| void | interpolate (const RobotState &to, double t, RobotState &state, const JointModelGroup *joint_group) const |
| void | interpolate (const RobotState &to, double t, RobotState &state, const JointModel *joint) const |
| void | enforceBounds () |
| void | enforceBounds (const JointModelGroup *joint_group) |
| void | enforceBounds (const JointModel *joint) |
| void | enforcePositionBounds (const JointModel *joint) |
| void | harmonizePositions () |
| Call harmonizePosition() for all joints / all joints in group / given joint. More... | |
| void | harmonizePositions (const JointModelGroup *joint_group) |
| void | harmonizePosition (const JointModel *joint) |
| void | enforceVelocityBounds (const JointModel *joint) |
| bool | satisfiesBounds (double margin=0.0) const |
| bool | satisfiesBounds (const JointModelGroup *joint_group, double margin=0.0) const |
| bool | satisfiesBounds (const JointModel *joint, double margin=0.0) const |
| bool | satisfiesPositionBounds (const JointModel *joint, double margin=0.0) const |
| bool | satisfiesVelocityBounds (const JointModel *joint, double margin=0.0) const |
| std::pair< double, const JointModel * > | getMinDistanceToPositionBounds () const |
| Get the minimm distance from this state to the bounds. The minimum distance and the joint for which this minimum is achieved are returned. More... | |
| std::pair< double, const JointModel * > | getMinDistanceToPositionBounds (const JointModelGroup *group) const |
| Get the minimm distance from a group in this state to the bounds. The minimum distance and the joint for which this minimum is achieved are returned. More... | |
| std::pair< double, const JointModel * > | getMinDistanceToPositionBounds (const std::vector< const JointModel * > &joints) const |
| Get the minimm distance from a set of joints in the state to the bounds. The minimum distance and the joint for which this minimum is achieved are returned. More... | |
| bool | isValidVelocityMove (const RobotState &other, const JointModelGroup *group, double dt) const |
| Check that the time to move between two waypoints is sufficient given velocity limits and time step. More... | |
Managing attached bodies | |
| void | attachBody (std::unique_ptr< AttachedBody > attached_body) |
| Add an attached body to this state. More... | |
| void | attachBody (AttachedBody *attached_body) |
| Add an attached body to this state. Ownership of the memory for the attached body is assumed by the state. More... | |
| void | attachBody (const std::string &id, const Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, const std::vector< shapes::ShapeConstPtr > &shapes, const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &shape_poses, const std::set< std::string > &touch_links, const std::string &link_name, const trajectory_msgs::msg::JointTrajectory &detach_posture=trajectory_msgs::msg::JointTrajectory(), const moveit::core::FixedTransformsMap &subframe_poses=moveit::core::FixedTransformsMap()) |
| Add an attached body to a link. More... | |
| void | attachBody (const std::string &id, const Eigen::Isometry3d &pose, const std::vector< shapes::ShapeConstPtr > &shapes, const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &shape_poses, const std::vector< std::string > &touch_links, const std::string &link_name, const trajectory_msgs::msg::JointTrajectory &detach_posture=trajectory_msgs::msg::JointTrajectory(), const moveit::core::FixedTransformsMap &subframe_poses=moveit::core::FixedTransformsMap()) |
| Add an attached body to a link. More... | |
| void | getAttachedBodies (std::vector< const AttachedBody * > &attached_bodies) const |
| Get all bodies attached to the model corresponding to this state. More... | |
| void | getAttachedBodies (std::vector< const AttachedBody * > &attached_bodies, const JointModelGroup *group) const |
| Get all bodies attached to a particular group the model corresponding to this state. More... | |
| void | getAttachedBodies (std::vector< const AttachedBody * > &attached_bodies, const LinkModel *link_model) const |
| Get all bodies attached to a particular link in the model corresponding to this state. More... | |
| bool | clearAttachedBody (const std::string &id) |
| Remove the attached body named id. Return false if the object was not found (and thus not removed). Return true on success. More... | |
| void | clearAttachedBodies (const LinkModel *link) |
| Clear the bodies attached to a specific link. More... | |
| void | clearAttachedBodies (const JointModelGroup *group) |
| Clear the bodies attached to a specific group. More... | |
| void | clearAttachedBodies () |
| Clear all attached bodies. This calls delete on the AttachedBody instances, if needed. More... | |
| const AttachedBody * | getAttachedBody (const std::string &name) const |
| Get the attached body named name. Return nullptr if not found. More... | |
| bool | hasAttachedBody (const std::string &id) const |
| Check if an attached body named id exists in this state. More... | |
| void | setAttachedBodyUpdateCallback (const AttachedBodyCallback &callback) |
Detailed Description
Representation of a robot's state. This includes position, velocity, acceleration and effort.
At the lowest level, a state is a collection of variables. Each variable has a name and can have position, velocity, acceleration and effort associated to it. Effort and acceleration share the memory area for efficiency reasons (one should not set both acceleration and effort in the same state and expect things to work). Often variables correspond to joint names as well (joints with one degree of freedom have one variable), but joints with multiple degrees of freedom have more variables. Operations are allowed at variable level, joint level (see JointModel) and joint group level (see JointModelGroup).
For efficiency reasons a state computes forward kinematics in a lazy fashion. This can sometimes lead to problems if the update() function was not called on the state.
Definition at line 89 of file robot_state.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ RobotState() [1/2]
| moveit::core::RobotState::RobotState | ( | const RobotModelConstPtr & | robot_model | ) |
A state can be constructed from a specified robot model. No values are initialized. Call setToDefaultValues() if a state needs to provide valid information.
Definition at line 60 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ ~RobotState()
| moveit::core::RobotState::~RobotState | ( | ) |
◆ RobotState() [2/2]
| moveit::core::RobotState::RobotState | ( | const RobotState & | other | ) |
Copy constructor.
Definition at line 79 of file robot_state.cpp.
Member Function Documentation
◆ attachBody() [1/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::attachBody | ( | AttachedBody * | attached_body | ) |
Add an attached body to this state. Ownership of the memory for the attached body is assumed by the state.
This only adds the given body to this RobotState instance. It does not change anything about other representations of the object elsewhere in the system. So if the body represents an object in a collision_detection::World (like from a planning_scene::PlanningScene), you will likely need to remove the corresponding object from that world to avoid having collisions detected against it.
- Note
- This version of the function (taking an AttachedBody pointer) does not copy the AttachedBody object, it just uses it directly. The AttachedBody object stores its position data internally. This means you should never attach a single AttachedBody instance to multiple RobotState instances, or the body positions will get corrupted. You need to make a fresh copy of the AttachedBody object for each RobotState you attach it to.
Definition at line 1016 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ attachBody() [2/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::attachBody | ( | const std::string & | id, |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | pose, | ||
| const std::vector< shapes::ShapeConstPtr > & | shapes, | ||
| const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d & | shape_poses, | ||
| const std::set< std::string > & | touch_links, | ||
| const std::string & | link_name, | ||
| const trajectory_msgs::msg::JointTrajectory & | detach_posture = trajectory_msgs::msg::JointTrajectory(), |
||
| const moveit::core::FixedTransformsMap & | subframe_poses = moveit::core::FixedTransformsMap() |
||
| ) |
Add an attached body to a link.
- Parameters
-
id The string id associated with the attached body pose The pose associated with the attached body shapes The shapes that make up the attached body shape_poses The transforms between the object pose and the attached body's shapes touch_links The set of links that the attached body is allowed to touch link_name The link to attach to detach_posture The posture of the gripper when placing the object subframe_poses Transforms to points of interest on the object (can be used as end effector link)
This only adds the given body to this RobotState instance. It does not change anything about other representations of the object elsewhere in the system. So if the body represents an object in a collision_detection::World (like from a planning_scene::PlanningScene), you will likely need to remove the corresponding object from that world to avoid having collisions detected against it.
Definition at line 1021 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ attachBody() [3/4]
|
inline |
Add an attached body to a link.
- Parameters
-
id The string id associated with the attached body pose The pose associated with the attached body shapes The shapes that make up the attached body shape_poses The transforms between the object pose and the attached body's shapes touch_links The set of links that the attached body is allowed to touch link_name The link to attach to detach_posture The posture of the gripper when placing the object subframe_poses Transforms to points of interest on the object (can be used as end effector link)
This only adds the given body to this RobotState instance. It does not change anything about other representations of the object elsewhere in the system. So if the body represents an object in a collision_detection::World (like from a planning_scene::PlanningScene), you will likely need to remove the corresponding object from that world to avoid having collisions detected against it.
Definition at line 1658 of file robot_state.h.
◆ attachBody() [4/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::attachBody | ( | std::unique_ptr< AttachedBody > | attached_body | ) |
Add an attached body to this state.
This only adds the given body to this RobotState instance. It does not change anything about other representations of the object elsewhere in the system. So if the body represents an object in a collision_detection::World (like from a planning_scene::PlanningScene), you will likely need to remove the corresponding object from that world to avoid having collisions detected against it.
Definition at line 1005 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ clearAttachedBodies() [1/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::clearAttachedBodies | ( | ) |
Clear all attached bodies. This calls delete on the AttachedBody instances, if needed.
Definition at line 1055 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ clearAttachedBodies() [2/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::clearAttachedBodies | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group | ) |
Clear the bodies attached to a specific group.
Definition at line 1080 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ clearAttachedBodies() [3/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::clearAttachedBodies | ( | const LinkModel * | link | ) |
Clear the bodies attached to a specific link.
Definition at line 1065 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ clearAttachedBody()
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::clearAttachedBody | ( | const std::string & | id | ) |
Remove the attached body named id. Return false if the object was not found (and thus not removed). Return true on success.
Definition at line 1095 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ computeAABB() [1/2]
|
inline |
Compute an axis-aligned bounding box that contains the current state. The format for aabb is (minx, maxx, miny, maxy, minz, maxz)
Definition at line 1705 of file robot_state.h.
◆ computeAABB() [2/2]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::computeAABB | ( | std::vector< double > & | aabb | ) | const |
Compute an axis-aligned bounding box that contains the current state. The format for aabb is (minx, maxx, miny, maxy, minz, maxz)
Definition at line 2058 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ computeCartesianPath() [1/3]
| double moveit::core::RobotState::computeCartesianPath | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| std::vector< RobotStatePtr > & | traj, | ||
| const LinkModel * | link, | ||
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | target, | ||
| bool | global_reference_frame, | ||
| double | max_step, | ||
| double | jump_threshold_factor, | ||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | validCallback = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions() |
||
| ) |
Compute the sequence of joint values that correspond to a straight Cartesian path, for a particular group.
In contrast to the previous function, the Cartesian path is specified as a target frame to be reached (target) for the origin of a robot link (link). The target frame is assumed to be either in a global reference frame or in the local reference frame of the link. In the latter case (global_reference_frame is false) the target is rotated accordingly. All other comments from the previous function apply.
NOTE: As of ROS-Melodic these are deprecated and should not be used
Definition at line 2036 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ computeCartesianPath() [2/3]
| double moveit::core::RobotState::computeCartesianPath | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| std::vector< RobotStatePtr > & | traj, | ||
| const LinkModel * | link, | ||
| const Eigen::Vector3d & | direction, | ||
| bool | global_reference_frame, | ||
| double | distance, | ||
| double | max_step, | ||
| double | jump_threshold_factor, | ||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | validCallback = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions() |
||
| ) |
Compute the sequence of joint values that correspond to a straight Cartesian path for a particular group.
The Cartesian path to be followed is specified as a direction of motion (direction, unit vector) for the origin The Cartesian path to be followed is specified as a direction of motion (direction, unit vector) for the origin of a robot link (link). The direction is assumed to be either in a global reference frame or in the local reference frame of the link. In the latter case (global_reference_frame is false) the direction is rotated accordingly. The link needs to move in a straight line, following the specified direction, for the desired distance. The resulting joint values are stored in the vector traj, one by one. The maximum distance in Cartesian space between consecutive points on the resulting path is specified in the MaxEEFStep struct which provides two fields: translation and rotation. If a validCallback is specified, this is passed to the internal call to setFromIK(). In case of IK failure, the computation of the path stops and the value returned corresponds to the distance that was computed and for which corresponding states were added to the path. At the end of the function call, the state of the group corresponds to the last attempted Cartesian pose.
During the computation of the trajectory, it is usually preferred if consecutive joint values do not 'jump' by a large amount in joint space, even if the Cartesian distance between the corresponding points is small as expected. To account for this, the jump_threshold struct is provided, which comprises three fields: jump_threshold_factor, revolute_jump_threshold and prismatic_jump_threshold. If either revolute_jump_threshold or prismatic_jump_threshold are non-zero, we test for absolute jumps. If jump_threshold_factor is non-zero, we test for relative jumps. Otherwise (all params are zero), jump detection is disabled.
For relative jump detection, the average joint-space distance between consecutive points in the trajectory is computed. If any individual joint-space motion delta is larger then this average distance by a factor of jump_threshold_factor, this step is considered a failure and the returned path is truncated up to just before the jump.
For absolute jump thresholds, if any individual joint-space motion delta is larger then revolute_jump_threshold for revolute joints or prismatic_jump_threshold for prismatic joints then this step is considered a failure and the returned path is truncated up to just before the jump.
NOTE: As of ROS-Melodic these are deprecated and should not be used
Definition at line 2025 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ computeCartesianPath() [3/3]
| double moveit::core::RobotState::computeCartesianPath | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| std::vector< RobotStatePtr > & | traj, | ||
| const LinkModel * | link, | ||
| const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d & | waypoints, | ||
| bool | global_reference_frame, | ||
| double | max_step, | ||
| double | jump_threshold_factor, | ||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | validCallback = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions() |
||
| ) |
Compute the sequence of joint values that perform a general Cartesian path.
In contrast to the previous functions, the Cartesian path is specified as a set of waypoints to be sequentially reached for the origin of a robot link (link). The waypoints are transforms given either in a global reference frame or in the local reference frame of the link at the immediately preceding waypoint. The link needs to move in a straight line between two consecutive waypoints. All other comments apply.
NOTE: As of ROS-Melodic these are deprecated and should not be used
Definition at line 2047 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ computeVariableVelocity() [1/2]
|
inline |
Given a twist for a particular link (tip), compute the corresponding velocity for every variable and store it in qdot.
Definition at line 1200 of file robot_state.h.
◆ computeVariableVelocity() [2/2]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::computeVariableVelocity | ( | const JointModelGroup * | jmg, |
| Eigen::VectorXd & | qdot, | ||
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | twist, | ||
| const LinkModel * | tip | ||
| ) | const |
Given a twist for a particular link (tip), compute the corresponding velocity for every variable and store it in qdot.
Definition at line 1413 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupAccelerations() [1/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::copyJointGroupAccelerations | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| double * | gstate | ||
| ) | const |
For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 638 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupAccelerations() [2/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::copyJointGroupAccelerations | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) | const |
For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 648 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupAccelerations() [3/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 914 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupAccelerations() [4/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 904 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupAccelerations() [5/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 928 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupAccelerations() [6/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the acceleration values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 891 of file robot_state.h.
◆ copyJointGroupPositions() [1/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::copyJointGroupPositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| double * | gstate | ||
| ) | const |
For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 560 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupPositions() [2/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::copyJointGroupPositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) | const |
For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 570 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupPositions() [3/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 714 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupPositions() [4/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 704 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupPositions() [5/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 728 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupPositions() [6/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the position values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 691 of file robot_state.h.
◆ copyJointGroupVelocities() [1/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::copyJointGroupVelocities | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| double * | gstate | ||
| ) | const |
For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 599 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupVelocities() [2/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::copyJointGroupVelocities | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) | const |
For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 609 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ copyJointGroupVelocities() [3/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 814 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupVelocities() [4/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 804 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupVelocities() [5/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 828 of file robot_state.h.

◆ copyJointGroupVelocities() [6/6]
|
inline |
For a given group, copy the velocity values of the variables that make up the group into another location, in the order that the variables are found in the group. This is not necessarily a contiguous block of memory in the RobotState itself, so we copy instead of returning a pointer.
Definition at line 791 of file robot_state.h.
◆ dirty()
|
inline |
Returns true if anything in this state is dirty.
Definition at line 1446 of file robot_state.h.
◆ dirtyCollisionBodyTransforms()
|
inline |
◆ dirtyJointTransform()
|
inline |
Definition at line 1430 of file robot_state.h.
◆ dirtyLinkTransforms()
|
inline |
◆ distance() [1/3]
|
inline |
Return the sum of joint distances to "other" state. An L1 norm. Only considers active joints.
Definition at line 1458 of file robot_state.h.
◆ distance() [2/3]
|
inline |
Return the sum of joint distances to "other" state. An L1 norm. Only considers active joints.
Definition at line 1467 of file robot_state.h.
◆ distance() [3/3]
| double moveit::core::RobotState::distance | ( | const RobotState & | other, |
| const JointModelGroup * | joint_group | ||
| ) | const |
Return the sum of joint distances to "other" state. An L1 norm. Only considers active joints.
Definition at line 950 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ dropAccelerations()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::dropAccelerations | ( | ) |
Remove accelerations from this state (this differs from setting them to zero)
Definition at line 267 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ dropDynamics()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::dropDynamics | ( | ) |
Reduce RobotState to kinematic information (remove velocity, acceleration and effort, if present)
Definition at line 277 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ dropEffort()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::dropEffort | ( | ) |
Remove effort values from this state (this differs from setting them to zero)
Definition at line 272 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ dropVelocities()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::dropVelocities | ( | ) |
Remove velocities from this state (this differs from setting them to zero)
Definition at line 262 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ enforceBounds() [1/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::enforceBounds | ( | ) |
◆ enforceBounds() [2/3]
|
inline |
◆ enforceBounds() [3/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::enforceBounds | ( | const JointModelGroup * | joint_group | ) |
◆ enforcePositionBounds()
|
inline |
Definition at line 1519 of file robot_state.h.
◆ enforceVelocityBounds()
|
inline |
Definition at line 1538 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getAttachedBodies() [1/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::getAttachedBodies | ( | std::vector< const AttachedBody * > & | attached_bodies | ) | const |
Get all bodies attached to the model corresponding to this state.
Definition at line 1031 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getAttachedBodies() [2/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::getAttachedBodies | ( | std::vector< const AttachedBody * > & | attached_bodies, |
| const JointModelGroup * | group | ||
| ) | const |
Get all bodies attached to a particular group the model corresponding to this state.
Definition at line 1039 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getAttachedBodies() [3/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::getAttachedBodies | ( | std::vector< const AttachedBody * > & | attached_bodies, |
| const LinkModel * | link_model | ||
| ) | const |
Get all bodies attached to a particular link in the model corresponding to this state.
Definition at line 1047 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getAttachedBody()
| const AttachedBody * moveit::core::RobotState::getAttachedBody | ( | const std::string & | name | ) | const |
Get the attached body named name. Return nullptr if not found.
Definition at line 993 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getCollisionBodyTransform() [1/4]
|
inline |
◆ getCollisionBodyTransform() [2/4]
|
inline |
◆ getCollisionBodyTransform() [3/4]
|
inline |
Get the link transform w.r.t. the root link (model frame) of the RobotModel. This is typically the root link of the URDF unless a virtual joint is present. Checks the cache and if there are any dirty (non-updated) transforms, first updates them as needed.
As opposed to the visual links in |getGlobalLinkTransform|, this function returns the collision link transform used for collision checking.
- Parameters
-
link_name name of link to lookup index specify which collision body to lookup, if more than one exists
Definition at line 1380 of file robot_state.h.
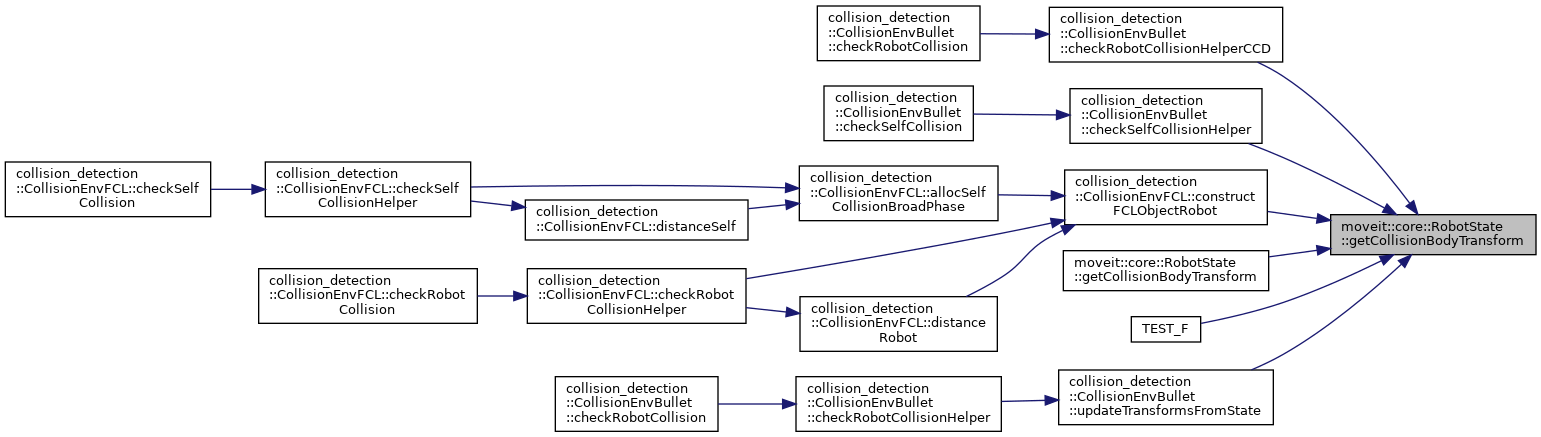
◆ getCollisionBodyTransform() [4/4]
|
inline |
◆ getFrameInfo()
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & moveit::core::RobotState::getFrameInfo | ( | const std::string & | frame_id, |
| const LinkModel *& | robot_link, | ||
| bool & | frame_found | ||
| ) | const |
Get the transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to the frame identified by frame_id.
If this frame is attached to a robot link, the link pointer is returned in robot_link. If frame_id was not found, frame_found is set to false and an identity transform is returned.
The returned transformation is always a valid isometry.
Definition at line 1129 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getFrameTransform() [1/2]
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & moveit::core::RobotState::getFrameTransform | ( | const std::string & | frame_id, |
| bool * | frame_found = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Get the transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to the frame identified by frame_id.
If frame_id was not found, frame_found is set to false and an identity transform is returned.
The returned transformation is always a valid isometry.
Definition at line 1109 of file robot_state.cpp.
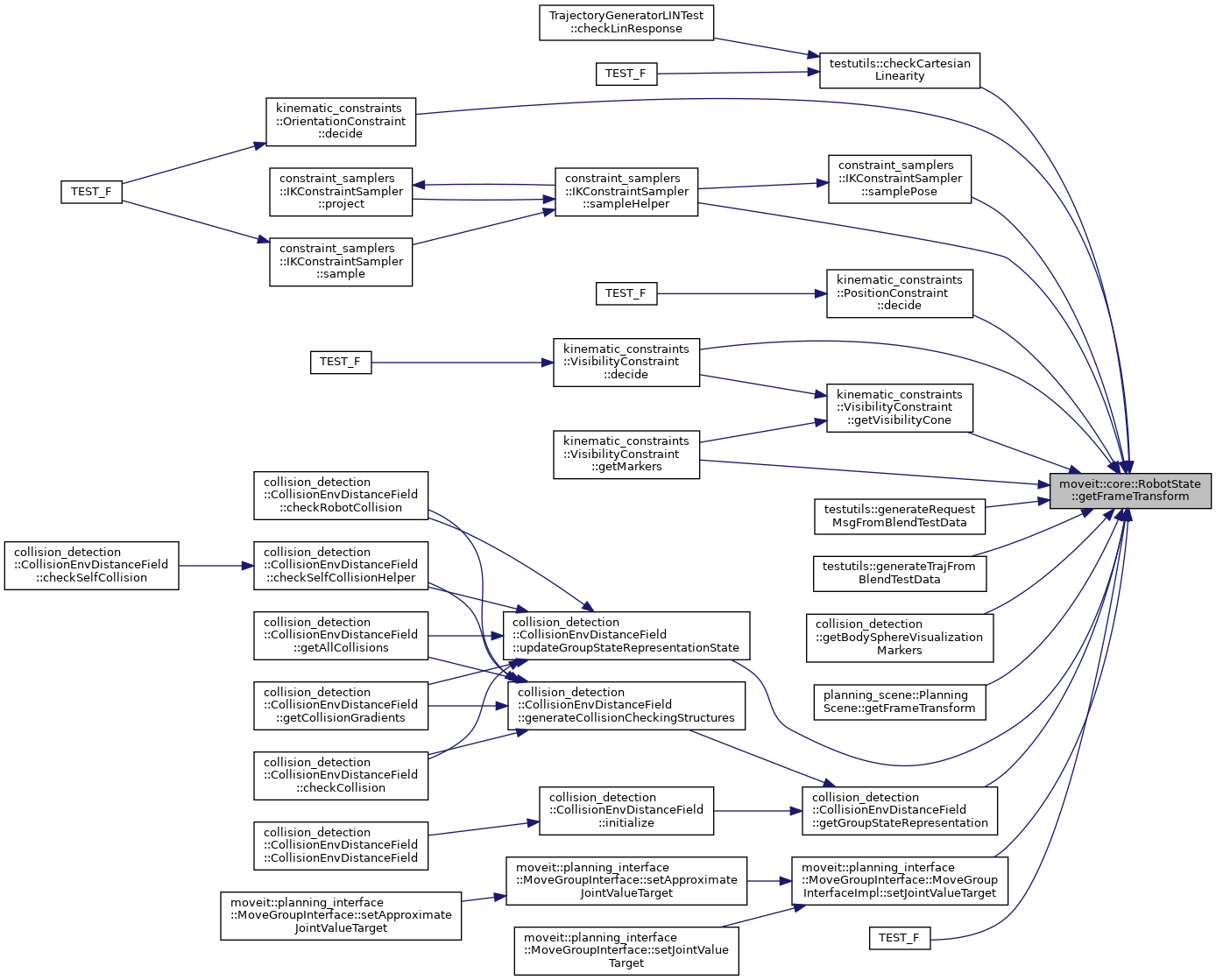
◆ getFrameTransform() [2/2]
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & moveit::core::RobotState::getFrameTransform | ( | const std::string & | frame_id, |
| bool * | frame_found = nullptr |
||
| ) | const |
Get the transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to the frame identified by frame_id.
If frame_id was not found, frame_found is set to false and an identity transform is returned.
The returned transformation is always a valid isometry.
Definition at line 1115 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ getGlobalLinkTransform() [1/4]
|
inline |
◆ getGlobalLinkTransform() [2/4]
|
inline |
◆ getGlobalLinkTransform() [3/4]
|
inline |
Get the link transform w.r.t. the root link (model frame) of the RobotModel. This is typically the root link of the URDF unless a virtual joint is present. Checks the cache and if there are any dirty (non-updated) transforms, first updates them as needed. A related, more comprehensive function is |getFrameTransform|, which additionally to link frames also searches for attached object frames and their subframes.
This will throw an exception if the passed link is not found
The returned transformation is always a valid isometry.
Definition at line 1340 of file robot_state.h.
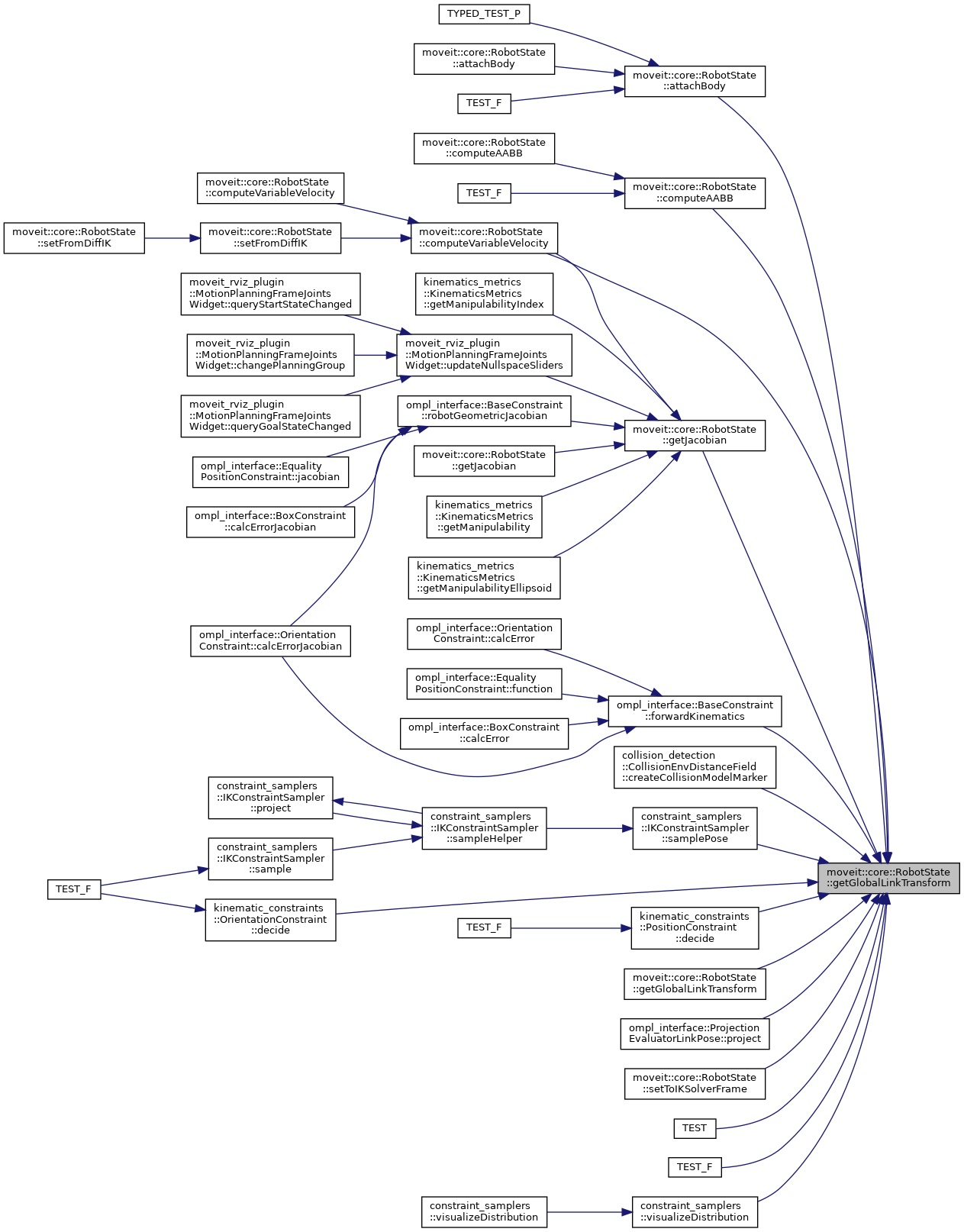
◆ getGlobalLinkTransform() [4/4]
|
inline |
◆ getJacobian() [1/4]
|
inline |
Compute the Jacobian with reference to the last link of a specified group. If the group is not a chain, an exception is thrown.
- Parameters
-
group The group to compute the Jacobian for reference_point_position The reference point position (with respect to the link specified in link_name)
- Returns
- The computed Jacobian.
Definition at line 1186 of file robot_state.h.
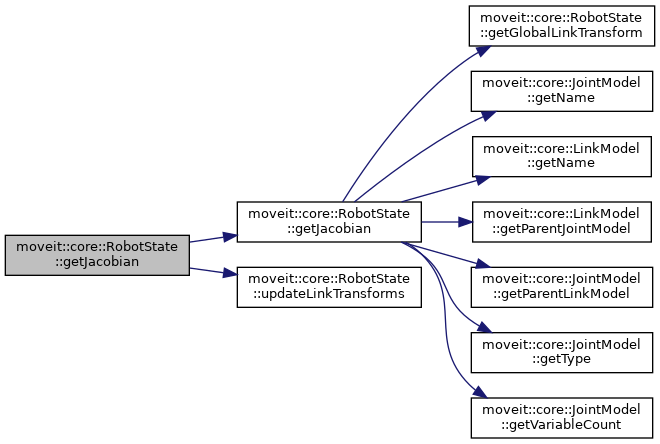
◆ getJacobian() [2/4]
| Eigen::MatrixXd moveit::core::RobotState::getJacobian | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::Vector3d & | reference_point_position = Eigen::Vector3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0) |
||
| ) | const |
Compute the Jacobian with reference to the last link of a specified group. If the group is not a chain, an exception is thrown.
- Parameters
-
group The group to compute the Jacobian for reference_point_position The reference point position (with respect to the link specified in link_name)
- Returns
- The computed Jacobian.
Definition at line 1283 of file robot_state.cpp.
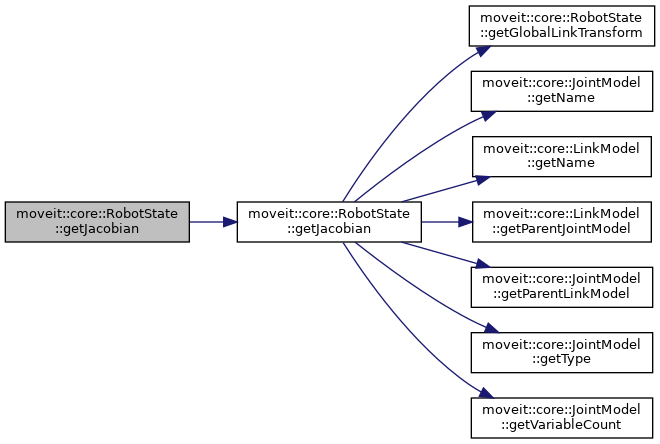
◆ getJacobian() [3/4]
|
inline |
Compute the Jacobian with reference to a particular point on a given link, for a specified group.
- Parameters
-
group The group to compute the Jacobian for link The link model to compute the Jacobian for reference_point_position The reference point position (with respect to the link specified in link) jacobian The resultant jacobian use_quaternion_representation Flag indicating if the Jacobian should use a quaternion representation (default is false)
- Returns
- True if jacobian was successfully computed, false otherwise
Definition at line 1163 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getJacobian() [4/4]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::getJacobian | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const LinkModel * | link, | ||
| const Eigen::Vector3d & | reference_point_position, | ||
| Eigen::MatrixXd & | jacobian, | ||
| bool | use_quaternion_representation = false |
||
| ) | const |
Compute the Jacobian with reference to a particular point on a given link, for a specified group.
- Parameters
-
group The group to compute the Jacobian for link The link model to compute the Jacobian for reference_point_position The reference point position (with respect to the link specified in link) jacobian The resultant jacobian use_quaternion_representation Flag indicating if the Jacobian should use a quaternion representation (default is false)
- Returns
- True if jacobian was successfully computed, false otherwise
Definition at line 1292 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getJointAccelerations() [1/2]
|
inline |
◆ getJointAccelerations() [2/2]
|
inline |
Definition at line 577 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getJointEffort() [1/2]
|
inline |
◆ getJointEffort() [2/2]
|
inline |
Definition at line 587 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getJointModel()
|
inline |
Get the model of a particular joint.
Definition at line 128 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getJointModelGroup()
|
inline |
Get the model of a particular joint group.
Definition at line 134 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getJointPositions() [1/2]
|
inline |
◆ getJointPositions() [2/2]
|
inline |
◆ getJointTransform() [1/4]
|
inline |
◆ getJointTransform() [2/4]
|
inline |
◆ getJointTransform() [3/4]
|
inline |
◆ getJointTransform() [4/4]
|
inline |
◆ getJointVelocities() [1/2]
|
inline |
◆ getJointVelocities() [2/2]
|
inline |
◆ getLinkModel()
|
inline |
Get the model of a particular link.
Definition at line 122 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getMinDistanceToPositionBounds() [1/3]
| std::pair< double, const JointModel * > moveit::core::RobotState::getMinDistanceToPositionBounds | ( | ) | const |
Get the minimm distance from this state to the bounds. The minimum distance and the joint for which this minimum is achieved are returned.
Definition at line 883 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ getMinDistanceToPositionBounds() [2/3]
| std::pair< double, const JointModel * > moveit::core::RobotState::getMinDistanceToPositionBounds | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group | ) | const |
Get the minimm distance from a group in this state to the bounds. The minimum distance and the joint for which this minimum is achieved are returned.
Definition at line 888 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ getMinDistanceToPositionBounds() [3/3]
| std::pair< double, const JointModel * > moveit::core::RobotState::getMinDistanceToPositionBounds | ( | const std::vector< const JointModel * > & | joints | ) | const |
Get the minimm distance from a set of joints in the state to the bounds. The minimum distance and the joint for which this minimum is achieved are returned.
Definition at line 894 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getRandomNumberGenerator()
|
inline |
Return the instance of a random number generator.
Definition at line 1712 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getRigidlyConnectedParentLinkModel()
| const LinkModel * moveit::core::RobotState::getRigidlyConnectedParentLinkModel | ( | const std::string & | frame, |
| const moveit::core::JointModelGroup * | jmg = nullptr |
||
| ) | const |
Get the latest link upwards the kinematic tree which is only connected via fixed joints.
This behaves the same as RobotModel::getRigidlyConnectedParentLinkModel, but can additionally resolve parents for attached objects / subframes.
Definition at line 831 of file robot_state.cpp.


◆ getRobotMarkers() [1/4]
|
inline |
Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot. Update the state first.
- Parameters
-
arr The returned marker array link_names The list of link names for which the markers should be created.
Definition at line 1782 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getRobotMarkers() [2/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::getRobotMarkers | ( | visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray & | arr, |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | link_names, | ||
| bool | include_attached = false |
||
| ) | const |
Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot.
- Parameters
-
arr The returned marker array link_names The list of link names for which the markers should be created.
Definition at line 1214 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getRobotMarkers() [3/4]
|
inline |
Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot. Update the state first.
- Parameters
-
arr The returned marker array link_names The list of link names for which the markers should be created. color The color for the marker ns The namespace for the markers dur The rclcpp::Duration for which the markers should stay visible
Definition at line 1763 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getRobotMarkers() [4/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::getRobotMarkers | ( | visualization_msgs::msg::MarkerArray & | arr, |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | link_names, | ||
| const std_msgs::msg::ColorRGBA & | color, | ||
| const std::string & | ns, | ||
| const rclcpp::Duration & | dur, | ||
| bool | include_attached = false |
||
| ) | const |
Get a MarkerArray that fully describes the robot markers for a given robot.
- Parameters
-
arr The returned marker array link_names The list of link names for which the markers should be created. color The color for the marker ns The namespace for the markers dur The rclcpp::Duration for which the markers should stay visible
Definition at line 1198 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getRobotModel()
|
inline |
Get the robot model this state is constructed for.
Definition at line 104 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getStateTreeString()
| std::string moveit::core::RobotState::getStateTreeString | ( | ) | const |
Definition at line 2253 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ getVariableAcceleration() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get the acceleration of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known.
Definition at line 395 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableAcceleration() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get the acceleration of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed
Definition at line 403 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableAccelerations() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get raw access to the accelerations of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames(). The area of memory overlaps with effort (effort and acceleration should not be set at the same time)
Definition at line 330 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableAccelerations() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get const raw access to the accelerations of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames()
Definition at line 338 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableCount()
|
inline |
Get the number of variables that make up this state.
Definition at line 110 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableEffort() [1/4]
|
inline |
Get raw access to the effort of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames(). The area of memory overlaps with accelerations (effort and acceleration should not be set at the same time)
Definition at line 428 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableEffort() [2/4]
|
inline |
Get const raw access to the effort of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames().
Definition at line 436 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableEffort() [3/4]
|
inline |
Get the effort of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known.
Definition at line 486 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableEffort() [4/4]
|
inline |
Get the effort of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed
Definition at line 494 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableNames()
|
inline |
Get the names of the variables that make up this state, in the order they are stored in memory.
Definition at line 116 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariablePosition() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get the position of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known.
Definition at line 207 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariablePosition() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get the position of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed
Definition at line 215 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariablePositions() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get a raw pointer to the positions of the variables stored in this state. Use carefully. If you change these values externally you need to make sure you trigger a forced update for the state by calling update(true).
Definition at line 147 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariablePositions() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get a raw pointer to the positions of the variables stored in this state.
Definition at line 154 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableVelocities() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get raw access to the velocities of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames()
Definition at line 236 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableVelocities() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get const access to the velocities of the variables that make up this state. The values are in the same order as reported by getVariableNames()
Definition at line 244 of file robot_state.h.
◆ getVariableVelocity() [1/2]
|
inline |
Get the velocity of a particular variable. An exception is thrown if the variable is not known.
Definition at line 296 of file robot_state.h.
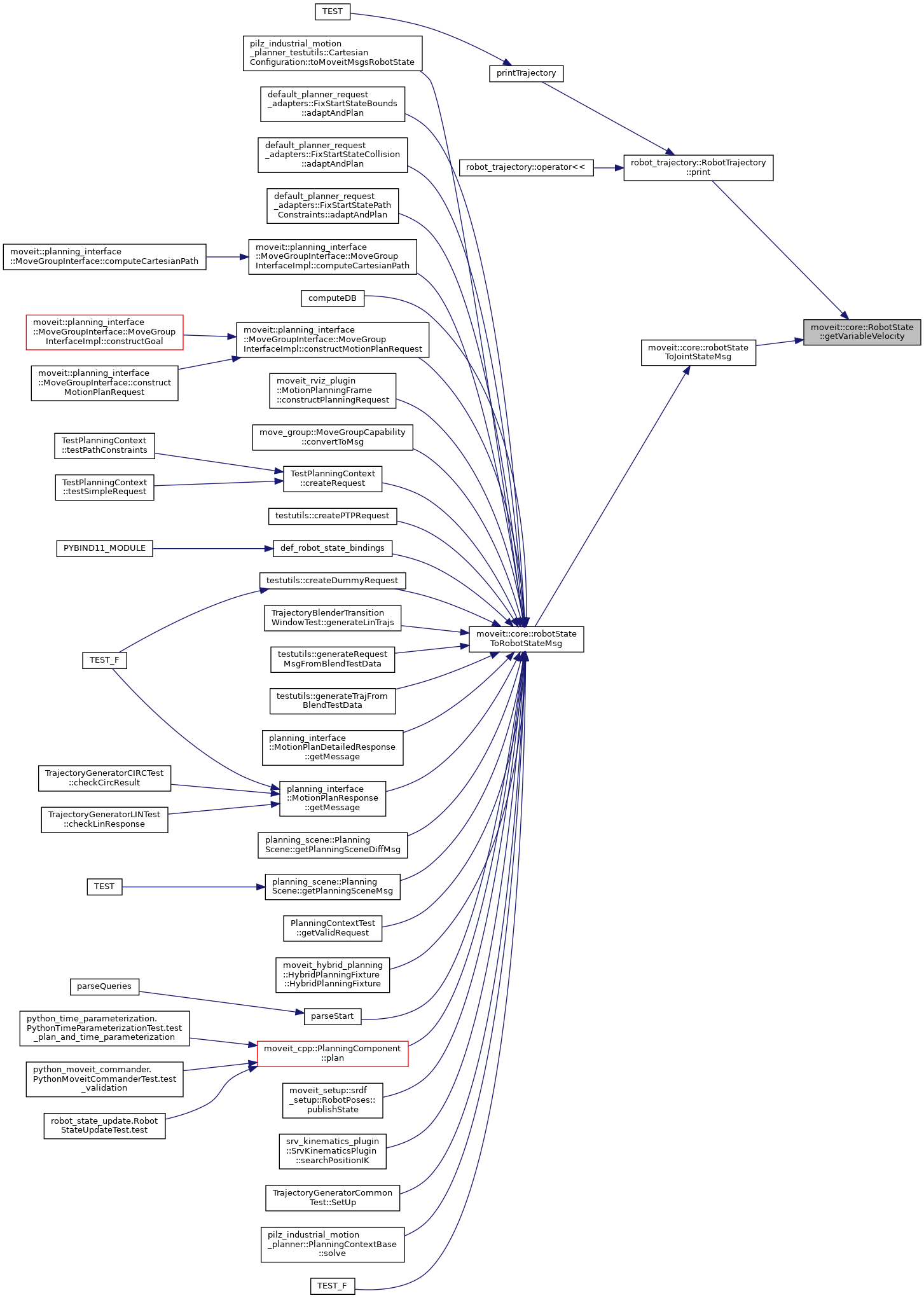
◆ getVariableVelocity() [2/2]
|
inline |
Get the velocity of a particular variable. The variable is specified by its index. No checks are performed for the validity of the index passed
Definition at line 304 of file robot_state.h.
◆ harmonizePosition()
|
inline |
Definition at line 1531 of file robot_state.h.
◆ harmonizePositions() [1/2]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::harmonizePositions | ( | ) |
Call harmonizePosition() for all joints / all joints in group / given joint.
Definition at line 871 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ harmonizePositions() [2/2]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::harmonizePositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | joint_group | ) |
◆ hasAccelerations()
|
inline |
By default, if accelerations are never set or initialized, the state remembers that there are no accelerations set. This is useful to know when serializing or copying the state. If hasAccelerations() reports true, hasEffort() will certainly report false.
Definition at line 322 of file robot_state.h.
◆ hasAttachedBody()
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::hasAttachedBody | ( | const std::string & | id | ) | const |
Check if an attached body named id exists in this state.
Definition at line 988 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ hasEffort()
|
inline |
By default, if effort is never set or initialized, the state remembers that there is no effort set. This is useful to know when serializing or copying the state. If hasEffort() reports true, hasAccelerations() will certainly report false.
Definition at line 420 of file robot_state.h.
◆ hasVelocities()
|
inline |
By default, if velocities are never set or initialized, the state remembers that there are no velocities set. This is useful to know when serializing or copying the state.
Definition at line 229 of file robot_state.h.
◆ integrateVariableVelocity()
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::integrateVariableVelocity | ( | const JointModelGroup * | jmg, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | qdot, | ||
| double | dt, | ||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn() |
||
| ) |
Given the velocities for the variables in this group (qdot) and an amount of time (dt), update the current state using the Euler forward method. If the constraint specified is satisfied, return true, otherwise return false.
Definition at line 1454 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ interpolate() [1/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::interpolate | ( | const RobotState & | to, |
| double | t, | ||
| RobotState & | state | ||
| ) | const |
Interpolate towards "to" state. Mimic joints are correctly updated and flags are set so that FK is recomputed when needed.
- Parameters
-
to interpolate to this state t a fraction in the range [0 1]. If 1, the result matches "to" state exactly. state holds the result
Definition at line 962 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ interpolate() [2/3]
|
inline |
Interpolate towards "to" state, but only for a single joint. Mimic joints are correctly updated and flags are set so that FK is recomputed when needed.
- Parameters
-
to interpolate to this state t a fraction in the range [0 1]. If 1, the result matches "to" state exactly. state holds the result joint interpolate only for this joint
Definition at line 1503 of file robot_state.h.
◆ interpolate() [3/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::interpolate | ( | const RobotState & | to, |
| double | t, | ||
| RobotState & | state, | ||
| const JointModelGroup * | joint_group | ||
| ) | const |
Interpolate towards "to" state, but only for the joints in the specified group. Mimic joints are correctly updated and flags are set so that FK is recomputed when needed.
- Parameters
-
to interpolate to this state t a fraction in the range [0 1]. If 1, the result matches "to" state exactly. state holds the result joint_group interpolate only for the joints in this group
Definition at line 971 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ invertVelocity()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::invertVelocity | ( | ) |
Invert velocity if present.
Definition at line 494 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ isValidVelocityMove()
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::isValidVelocityMove | ( | const RobotState & | other, |
| const JointModelGroup * | group, | ||
| double | dt | ||
| ) | const |
Check that the time to move between two waypoints is sufficient given velocity limits and time step.
- Parameters
-
other - robot state to compare joint positions against group - planning group to compare joint positions against dt - time step between the two points
Definition at line 930 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ knowsFrameTransform()
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::knowsFrameTransform | ( | const std::string & | frame_id | ) | const |
Check if a transformation matrix from the model frame (root of model) to frame frame_id is known.
Definition at line 1177 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ operator=()
| RobotState & moveit::core::RobotState::operator= | ( | const RobotState & | other | ) |
Copy operator.
Definition at line 139 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ printDirtyInfo()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::printDirtyInfo | ( | std::ostream & | out = std::cout | ) | const |
◆ printStateInfo()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::printStateInfo | ( | std::ostream & | out = std::cout | ) | const |
Definition at line 2164 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ printStatePositions()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::printStatePositions | ( | std::ostream & | out = std::cout | ) | const |
Definition at line 2093 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ printStatePositionsWithJointLimits()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::printStatePositionsWithJointLimits | ( | const moveit::core::JointModelGroup * | jmg, |
| std::ostream & | out = std::cout |
||
| ) | const |
Output to console the current state of the robot's joint limits.
Definition at line 2100 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ printTransform()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::printTransform | ( | const Eigen::Isometry3d & | transform, |
| std::ostream & | out = std::cout |
||
| ) | const |
◆ printTransforms()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::printTransforms | ( | std::ostream & | out = std::cout | ) | const |
Definition at line 2224 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ satisfiesBounds() [1/3]
|
inline |
◆ satisfiesBounds() [2/3]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::satisfiesBounds | ( | const JointModelGroup * | joint_group, |
| double | margin = 0.0 |
||
| ) | const |
◆ satisfiesBounds() [3/3]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::satisfiesBounds | ( | double | margin = 0.0 | ) | const |
◆ satisfiesPositionBounds()
|
inline |
Definition at line 1549 of file robot_state.h.
◆ satisfiesVelocityBounds()
|
inline |
Definition at line 1553 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setAttachedBodyUpdateCallback()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setAttachedBodyUpdateCallback | ( | const AttachedBodyCallback & | callback | ) |
Definition at line 983 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setFromDiffIK() [1/2]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromDiffIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | twist, | ||
| const std::string & | tip, | ||
| double | dt, | ||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn() |
||
| ) |
Set the joint values from a Cartesian velocity applied during a time dt.
- Parameters
-
group the group of joints this function operates on twist a Cartesian velocity on the 'tip' frame tip the frame for which the twist is given dt a time interval (seconds) st a secondary task computation function
Definition at line 1397 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setFromDiffIK() [2/2]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromDiffIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const geometry_msgs::msg::Twist & | twist, | ||
| const std::string & | tip, | ||
| double | dt, | ||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn() |
||
| ) |
Set the joint values from a Cartesian velocity applied during a time dt.
- Parameters
-
group the group of joints this function operates on twist a Cartesian velocity on the 'tip' frame tip the frame for which the twist is given dt a time interval (seconds) st a secondary task computation function
Definition at line 1405 of file robot_state.cpp.
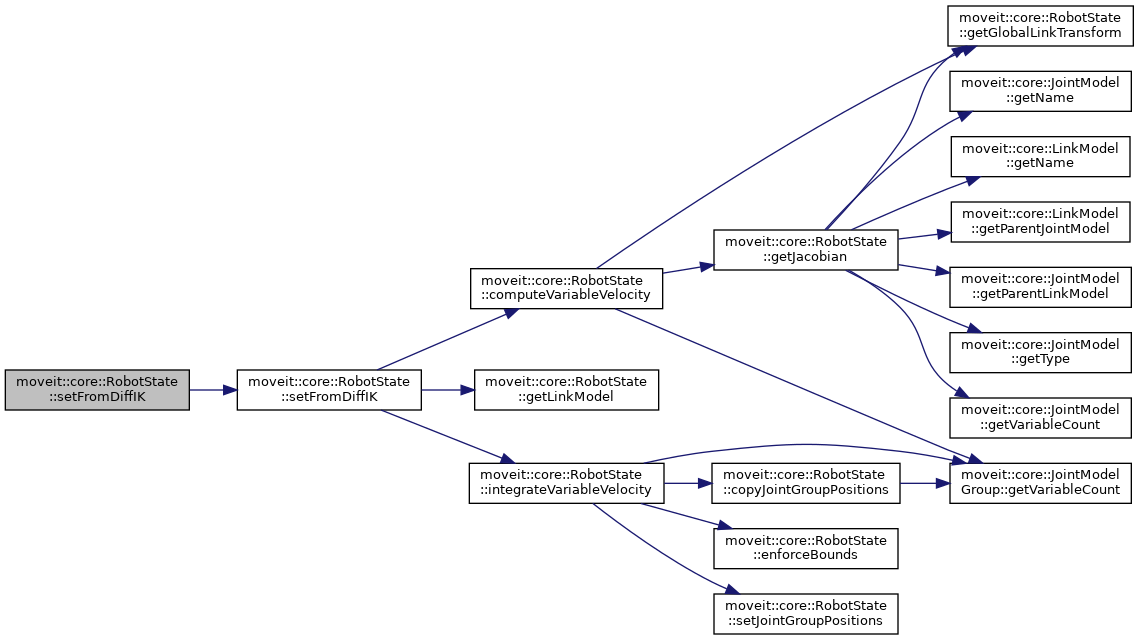
◆ setFromIK() [1/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | pose, | ||
| const std::string & | tip, | ||
| const std::vector< double > & | consistency_limits, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
pose The pose the last link in the chain needs to achieve tip The name of the frame for which IK is attempted. consistency_limits This specifies the desired distance between the solution and the seed state timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
Definition at line 1562 of file robot_state.cpp.
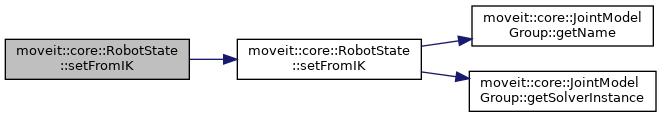
◆ setFromIK() [2/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | pose, | ||
| const std::string & | tip, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
pose The pose the last link in the chain needs to achieve timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
Definition at line 1513 of file robot_state.cpp.
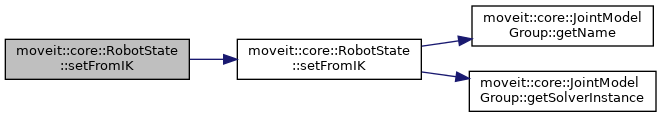
◆ setFromIK() [3/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | pose, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
pose The pose the last link in the chain needs to achieve tip The name of the link the pose is specified for timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt
Definition at line 1498 of file robot_state.cpp.
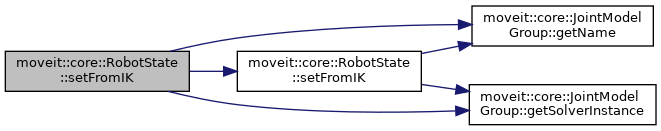
◆ setFromIK() [4/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d & | poses, | ||
| const std::vector< std::string > & | tips, | ||
| const std::vector< std::vector< double >> & | consistency_limits, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
Warning: This function inefficiently copies all transforms around. If the group consists of a set of sub-groups that are each a chain and a solver is available for each sub-group, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The poses are assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. The poses are assumed to be in the same order as the order of the sub-groups in this group. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
poses The poses the last link in each chain needs to achieve tips The names of the frames for which IK is attempted. consistency_limits This specifies the desired distance between the solution and the seed state timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
◆ setFromIK() [5/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d & | poses, | ||
| const std::vector< std::string > & | tips, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
Warning: This function inefficiently copies all transforms around. If the group consists of a set of sub-groups that are each a chain and a solver is available for each sub-group, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The poses are assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. The poses are assumed to be in the same order as the order of the sub-groups in this group. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
poses The poses the last link in each chain needs to achieve tips The names of the frames for which IK is attempted. timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
Definition at line 1581 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setFromIK() [6/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose & | pose, | ||
| const std::string & | tip, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
pose The pose the tip link in the chain needs to achieve tip The name of the link the pose is specified for timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
Definition at line 1487 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setFromIK() [7/7]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIK | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose & | pose, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn & | cost_function = kinematics::KinematicsBase::IKCostFn() |
||
| ) |
If the group this state corresponds to is a chain and a solver is available, then the joint values can be set by computing inverse kinematics. The pose is assumed to be in the reference frame of the kinematic model. Returns true on success.
- Parameters
-
pose The pose the last link in the chain needs to achieve timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
Definition at line 1473 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setFromIKSubgroups()
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setFromIKSubgroups | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d & | poses, | ||
| const std::vector< std::string > & | tips, | ||
| const std::vector< std::vector< double >> & | consistency_limits, | ||
| double | timeout = 0.0, |
||
| const GroupStateValidityCallbackFn & | constraint = GroupStateValidityCallbackFn(), |
||
| const kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions & | options = kinematics::KinematicsQueryOptions() |
||
| ) |
setFromIK for multiple poses and tips (end effectors) when no solver exists for the jmg that can solver for non-chain kinematics. In this case, we divide the group into subgroups and do IK solving individually
- Parameters
-
poses The poses the last link in each chain needs to achieve tips The names of the frames for which IK is attempted. consistency_limits This specifies the desired distance between the solution and the seed state timeout The timeout passed to the kinematics solver on each attempt constraint A state validity constraint to be required for IK solutions
Definition at line 1821 of file robot_state.cpp.
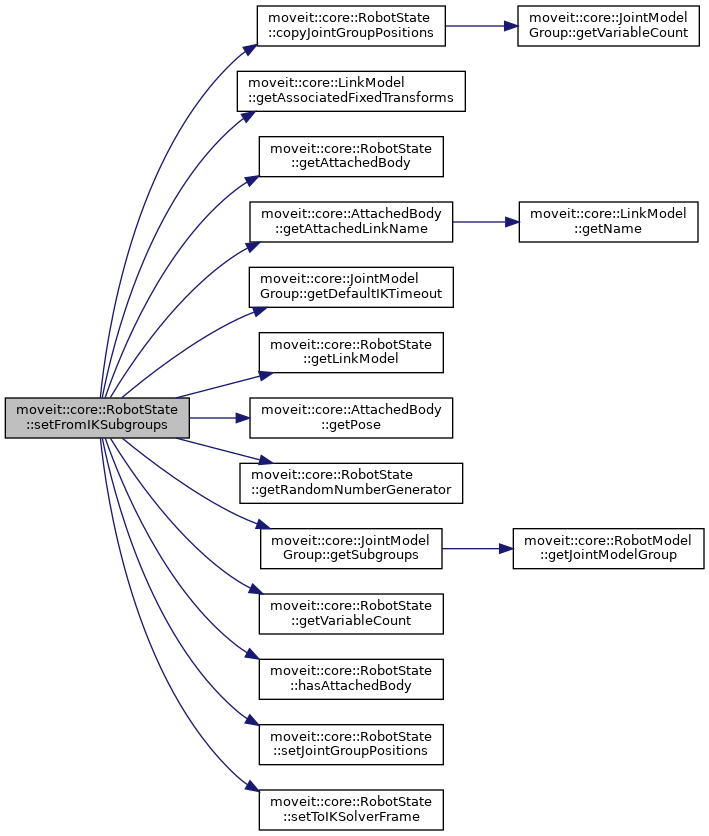
◆ setJointEfforts()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointEfforts | ( | const JointModel * | joint, |
| const double * | effort | ||
| ) |
◆ setJointGroupAccelerations() [1/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupAccelerations | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const double * | gstate | ||
| ) |
Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 617 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupAccelerations() [2/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupAccelerations | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) |
Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 630 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupAccelerations() [3/6]
|
inline |
Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 866 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupAccelerations() [4/6]
|
inline |
Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 848 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupAccelerations() [5/6]
|
inline |
Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 877 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupAccelerations() [6/6]
|
inline |
Given accelerations for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 857 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupActivePositions() [1/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupActivePositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) |
Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 548 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupActivePositions() [2/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupActivePositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const std::vector< double > & | gstate | ||
| ) |
Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 536 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupActivePositions() [3/4]
|
inline |
Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 678 of file robot_state.h.

◆ setJointGroupActivePositions() [4/4]
|
inline |
Given positions for the variables of active joints that make up a group, in the order found in the group (excluding values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 660 of file robot_state.h.

◆ setJointGroupPositions() [1/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupPositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const double * | gstate | ||
| ) |
Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 515 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupPositions() [2/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupPositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) |
Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 528 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupPositions() [3/6]
|
inline |
Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 626 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupPositions() [4/6]
|
inline |
Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 605 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupPositions() [5/6]
|
inline |
Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 638 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupPositions() [6/6]
|
inline |
Given positions for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 614 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupVelocities() [1/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupVelocities | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const double * | gstate | ||
| ) |
Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 578 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupVelocities() [2/6]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setJointGroupVelocities | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const Eigen::VectorXd & | values | ||
| ) |
Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 591 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setJointGroupVelocities() [3/6]
|
inline |
Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 766 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupVelocities() [4/6]
|
inline |
Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 748 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupVelocities() [5/6]
|
inline |
Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 777 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointGroupVelocities() [6/6]
|
inline |
Given velocities for the variables that make up a group, in the order found in the group (including values of mimic joints), set those as the new values that correspond to the group.
Definition at line 757 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setJointPositions() [1/6]
|
inline |
◆ setJointPositions() [2/6]
|
inline |
◆ setJointPositions() [3/6]
|
inline |
◆ setJointPositions() [4/6]
|
inline |
◆ setJointPositions() [5/6]
|
inline |
◆ setJointPositions() [6/6]
|
inline |
◆ setJointVelocities()
|
inline |
◆ setToDefaultValues() [1/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToDefaultValues | ( | ) |
Set all joints to their default positions. The default position is 0, or if that is not within bounds then half way between min and max bound.
Definition at line 361 of file robot_state.cpp.
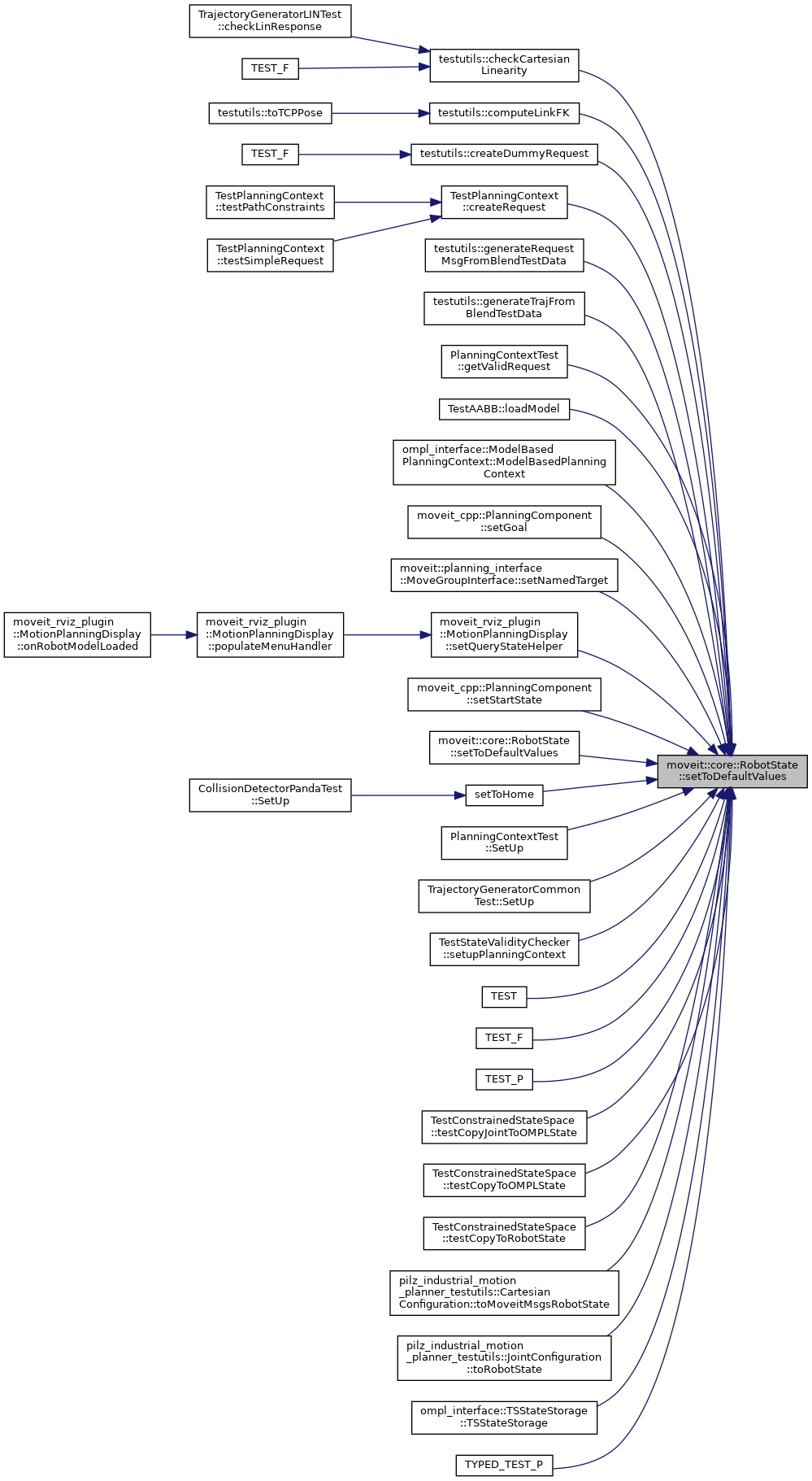
◆ setToDefaultValues() [2/3]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setToDefaultValues | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const std::string & | name | ||
| ) |
Set the joints in group to the position name defined in the SRDF.
Definition at line 353 of file robot_state.cpp.
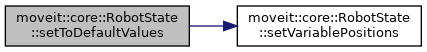
◆ setToDefaultValues() [3/3]
|
inline |
◆ setToIKSolverFrame() [1/2]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setToIKSolverFrame | ( | Eigen::Isometry3d & | pose, |
| const kinematics::KinematicsBaseConstPtr & | solver | ||
| ) |
Transform pose from the robot model's base frame to the reference frame of the IK solver.
- Parameters
-
pose - the input to change solver - a kin solver whose base frame is important to us
- Returns
- true if no error
Definition at line 1540 of file robot_state.cpp.
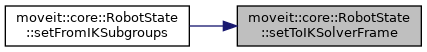
◆ setToIKSolverFrame() [2/2]
| bool moveit::core::RobotState::setToIKSolverFrame | ( | Eigen::Isometry3d & | pose, |
| const std::string & | ik_frame | ||
| ) |
Transform pose from the robot model's base frame to the reference frame of the IK solver.
- Parameters
-
pose - the input to change ik_frame - the name of frame of reference of base of ik solver
- Returns
- true if no error
Definition at line 1545 of file robot_state.cpp.
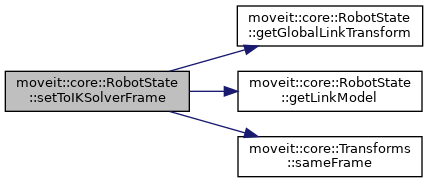
◆ setToRandomPositions() [1/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositions | ( | ) |
Set all joints to random values. Values will be within default bounds.
Definition at line 284 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setToRandomPositions() [2/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group | ) |
Set all joints in group to random values. Values will be within default bounds.
Definition at line 293 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setToRandomPositions() [3/3]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositions | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator & | rng | ||
| ) |
Set all joints in group to random values using a specified random number generator. Values will be within default bounds.
Definition at line 300 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setToRandomPositionsNearBy() [1/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositionsNearBy | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const RobotState & | seed, | ||
| const std::vector< double > & | distances | ||
| ) |
Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed. distances MUST have the same size as group.getActiveJointModels(). Each value in distances is the maximum amount the corresponding active joint in group will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds.
Definition at line 308 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setToRandomPositionsNearBy() [2/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositionsNearBy | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const RobotState & | seed, | ||
| const std::vector< double > & | distances, | ||
| random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator & | rng | ||
| ) |
Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed, using a specified random number generator. distances MUST have the same size as group.getActiveJointModels(). Each value in distances is the maximum amount the corresponding active joint in group will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds.
Definition at line 317 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setToRandomPositionsNearBy() [3/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositionsNearBy | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const RobotState & | seed, | ||
| double | distance | ||
| ) |
Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed. distance is the maximum amount each joint value will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds.
Definition at line 332 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ setToRandomPositionsNearBy() [4/4]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setToRandomPositionsNearBy | ( | const JointModelGroup * | group, |
| const RobotState & | seed, | ||
| double | distance, | ||
| random_numbers::RandomNumberGenerator & | rng | ||
| ) |
Set all joints in group to random values near the value in seed, using a specified random number generator. distance is the maximum amount each joint value will vary from the corresponding value in seed. \distance represents meters for prismatic/postitional joints and radians for revolute/orientation joints. Resulting values are clamped within default bounds.
Definition at line 340 of file robot_state.cpp.

◆ setVariableAcceleration() [1/2]
|
inline |
Set the acceleration of a variable. If an unknown variable name is specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 381 of file robot_state.h.

◆ setVariableAcceleration() [2/2]
|
inline |
Set the acceleration of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable)
Definition at line 388 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableAccelerations() [1/5]
|
inline |
Given an array with acceleration values for all variables, set those values as the accelerations in this state.
Definition at line 348 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableAccelerations() [2/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableAccelerations | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map | ) |
Set the accelerations of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 448 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableAccelerations() [3/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableAccelerations | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map, |
| std::vector< std::string > & | missing_variables | ||
| ) |
Set the accelerations of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set.
Definition at line 455 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableAccelerations() [4/5]
|
inline |
Given an array with acceleration values for all variables, set those values as the accelerations in this state.
Definition at line 359 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableAccelerations() [5/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableAccelerations | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | variable_names, |
| const std::vector< double > & | variable_acceleration | ||
| ) |
Set the accelerations of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 462 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableEffort() [1/7]
|
inline |
Given an array with effort values for all variables, set those values as the effort in this state.
Definition at line 445 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableEffort() [2/7]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableEffort | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map | ) |
Set the effort of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 471 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableEffort() [3/7]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableEffort | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map, |
| std::vector< std::string > & | missing_variables | ||
| ) |
Set the effort of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set.
Definition at line 478 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableEffort() [4/7]
|
inline |
Set the effort of a variable. If an unknown variable name is specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 472 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableEffort() [5/7]
|
inline |
Given an array with effort values for all variables, set those values as the effort in this state.
Definition at line 454 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableEffort() [6/7]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableEffort | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | variable_names, |
| const std::vector< double > & | variable_acceleration | ||
| ) |
Set the effort of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 485 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableEffort() [7/7]
|
inline |
Set the effort of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable)
Definition at line 479 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariablePosition() [1/2]
|
inline |
Set the position of a single variable. An exception is thrown if the variable name is not known.
Definition at line 188 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariablePosition() [2/2]
|
inline |
Set the position of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable)
Definition at line 195 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariablePositions() [1/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariablePositions | ( | const double * | position | ) |
It is assumed positions is an array containing the new positions for all variables in this state. Those values are copied into the state.
Definition at line 370 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariablePositions() [2/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariablePositions | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map | ) |
Set the positions of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 382 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariablePositions() [3/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariablePositions | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map, |
| std::vector< std::string > & | missing_variables | ||
| ) |
Set the positions of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set.
Definition at line 405 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariablePositions() [4/5]
|
inline |
It is assumed positions is an array containing the new positions for all variables in this state. Those values are copied into the state.
Definition at line 167 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariablePositions() [5/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariablePositions | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | variable_names, |
| const std::vector< double > & | variable_position | ||
| ) |
Set the positions of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set.
Definition at line 412 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableValues()
|
inline |
◆ setVariableVelocities() [1/5]
|
inline |
Given an array with velocity values for all variables, set those values as the velocities in this state.
Definition at line 253 of file robot_state.h.
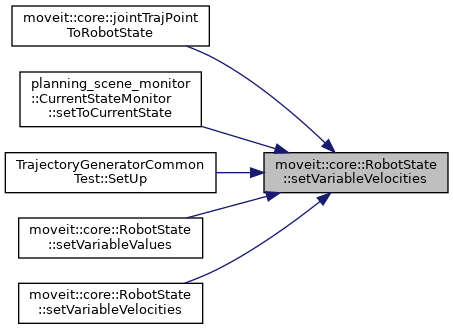
◆ setVariableVelocities() [2/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableVelocities | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map | ) |
Set the velocities of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 425 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableVelocities() [3/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableVelocities | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_map, |
| std::vector< std::string > & | missing_variables | ||
| ) |
Set the velocities of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown. Additionally, missing_variables is filled with the names of the variables that are not set.
Definition at line 432 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableVelocities() [4/5]
|
inline |
Given an array with velocity values for all variables, set those values as the velocities in this state.
Definition at line 261 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableVelocities() [5/5]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::setVariableVelocities | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | variable_names, |
| const std::vector< double > & | variable_velocity | ||
| ) |
Set the velocities of a set of variables. If unknown variable names are specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 439 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ setVariableVelocity() [1/2]
|
inline |
Set the velocity of a variable. If an unknown variable name is specified, an exception is thrown.
Definition at line 282 of file robot_state.h.
◆ setVariableVelocity() [2/2]
|
inline |
Set the velocity of a single variable. The variable is specified by its index (a value associated by the RobotModel to each variable)
Definition at line 289 of file robot_state.h.
◆ update()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::update | ( | bool | force = false | ) |
Update all transforms.
Definition at line 656 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ updateCollisionBodyTransforms()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::updateCollisionBodyTransforms | ( | ) |
Update the transforms for the collision bodies. This call is needed before calling collision checking. If updating link transforms or joint transforms is needed, the corresponding updates are also triggered.
Definition at line 669 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ updateLinkTransforms()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::updateLinkTransforms | ( | ) |
Update the reference frame transforms for links. This call is needed before using the transforms of links for coordinate transforms.
Definition at line 697 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ updateStateWithLinkAt() [1/2]
| void moveit::core::RobotState::updateStateWithLinkAt | ( | const LinkModel * | link, |
| const Eigen::Isometry3d & | transform, | ||
| bool | backward = false |
||
| ) |
Update the state after setting a particular link to the input global transform pose.
Definition at line 750 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ updateStateWithLinkAt() [2/2]
|
inline |
Update the state after setting a particular link to the input global transform pose.
This "warps" the given link to the given pose, neglecting the joint values of its parent joint. The link transforms of link and all its descendants are updated, but not marked as dirty, although they do not match the joint values anymore! Collision body transforms are not yet updated, but marked dirty only. Use update(false) or updateCollisionBodyTransforms() to update them as well.
Definition at line 1314 of file robot_state.h.
◆ zeroAccelerations()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::zeroAccelerations | ( | ) |
Set all accelerations to 0.0.
Definition at line 250 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ zeroEffort()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::zeroEffort | ( | ) |
Set all effort values to 0.0.
Definition at line 256 of file robot_state.cpp.
◆ zeroVelocities()
| void moveit::core::RobotState::zeroVelocities | ( | ) |
Set all velocities to 0.0.
Definition at line 244 of file robot_state.cpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- moveit_core/robot_state/include/moveit/robot_state/robot_state.h
- moveit_core/robot_state/src/robot_state.cpp