Client class to conveniently use the ROS interfaces provided by the move_group node. More...
#include <moveit/planning_interface/move_group_interface.h>
Classes | |
| class | MoveGroupInterfaceImpl |
| struct | Options |
| Specification of options to use when constructing the MoveGroupInterface class. More... | |
| struct | Plan |
| The representation of a motion plan (as ROS messasges) More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| MOVEIT_STRUCT_FORWARD (Plan) | |
| MoveGroupInterface (const rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr &node, const Options &opt, const std::shared_ptr< tf2_ros::Buffer > &tf_buffer=std::shared_ptr< tf2_ros::Buffer >(), const rclcpp::Duration &wait_for_servers=rclcpp::Duration::from_seconds(-1)) | |
| Construct a MoveGroupInterface instance call using a specified set of options opt. More... | |
| MoveGroupInterface (const rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr &node, const std::string &group, const std::shared_ptr< tf2_ros::Buffer > &tf_buffer=std::shared_ptr< tf2_ros::Buffer >(), const rclcpp::Duration &wait_for_servers=rclcpp::Duration::from_seconds(-1)) | |
| Construct a client for the MoveGroup action for a particular group. More... | |
| ~MoveGroupInterface () | |
| MoveGroupInterface (const MoveGroupInterface &)=delete | |
| This class owns unique resources (e.g. action clients, threads) and its not very meaningful to copy. Pass by references, move it, or simply create multiple instances where required. More... | |
| MoveGroupInterface & | operator= (const MoveGroupInterface &)=delete |
| MoveGroupInterface (MoveGroupInterface &&other) noexcept | |
| MoveGroupInterface & | operator= (MoveGroupInterface &&other) noexcept |
| const std::string & | getName () const |
| Get the name of the group this instance operates on. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getNamedTargets () const |
| Get the names of the named robot states available as targets, both either remembered states or default states from srdf. More... | |
| moveit::core::RobotModelConstPtr | getRobotModel () const |
| Get the RobotModel object. More... | |
| rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr | getNodeHandle () |
| Get the ROS node handle of this instance operates on. More... | |
| const std::string & | getPlanningFrame () const |
| Get the name of the frame in which the robot is planning. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getJointModelGroupNames () const |
| Get the available planning group names. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getJointNames () const |
| Get vector of names of joints available in move group. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getLinkNames () const |
| Get vector of names of links available in move group. More... | |
| std::map< std::string, double > | getNamedTargetValues (const std::string &name) const |
| Get the joint angles for targets specified by name. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getActiveJoints () const |
| Get only the active (actuated) joints this instance operates on. More... | |
| const std::vector< std::string > & | getJoints () const |
| Get all the joints this instance operates on (including fixed joints) More... | |
| unsigned int | getVariableCount () const |
| Get the number of variables used to describe the state of this group. This is larger or equal to the number of DOF. More... | |
| bool | getInterfaceDescriptions (std::vector< moveit_msgs::msg::PlannerInterfaceDescription > &desc) const |
| Get the descriptions of all planning plugins loaded by the action server. More... | |
| bool | getInterfaceDescription (moveit_msgs::msg::PlannerInterfaceDescription &desc) const |
| Get the description of the default planning plugin loaded by the action server. More... | |
| std::map< std::string, std::string > | getPlannerParams (const std::string &planner_id, const std::string &group="") const |
| Get the planner parameters for given group and planner_id. More... | |
| void | setPlannerParams (const std::string &planner_id, const std::string &group, const std::map< std::string, std::string > ¶ms, bool bReplace=false) |
| Set the planner parameters for given group and planner_id. More... | |
| std::string | getDefaultPlanningPipelineId () const |
| void | setPlanningPipelineId (const std::string &pipeline_id) |
| Specify a planning pipeline to be used for further planning. More... | |
| const std::string & | getPlanningPipelineId () const |
| Get the current planning_pipeline_id. More... | |
| std::string | getDefaultPlannerId (const std::string &group="") const |
| Get the default planner of the current planning pipeline for the given group (or the pipeline's default) More... | |
| void | setPlannerId (const std::string &planner_id) |
| Specify a planner to be used for further planning. More... | |
| const std::string & | getPlannerId () const |
| Get the current planner_id. More... | |
| void | setPlanningTime (double seconds) |
| Specify the maximum amount of time to use when planning. More... | |
| void | setNumPlanningAttempts (unsigned int num_planning_attempts) |
| Set the number of times the motion plan is to be computed from scratch before the shortest solution is returned. The default value is 1. More... | |
| void | setMaxVelocityScalingFactor (double max_velocity_scaling_factor) |
| Set a scaling factor for optionally reducing the maximum joint velocity. Allowed values are in (0,1]. The maximum joint velocity specified in the robot model is multiplied by the factor. If the value is 0, it is set to the default value, which is defined in joint_limits.yaml of the moveit_config. If the value is greater than 1, it is set to 1.0. More... | |
| void | setMaxAccelerationScalingFactor (double max_acceleration_scaling_factor) |
| Set a scaling factor for optionally reducing the maximum joint acceleration. Allowed values are in (0,1]. The maximum joint acceleration specified in the robot model is multiplied by the factor. If the value is 0, it is set to the default value, which is defined in joint_limits.yaml of the moveit_config. If the value is greater than 1, it is set to 1.0. More... | |
| double | getPlanningTime () const |
| Get the number of seconds set by setPlanningTime() More... | |
| double | getGoalJointTolerance () const |
| Get the tolerance that is used for reaching a joint goal. This is distance for each joint in configuration space. More... | |
| double | getGoalPositionTolerance () const |
| Get the tolerance that is used for reaching a position goal. This is be the radius of a sphere where the end-effector must reach. More... | |
| double | getGoalOrientationTolerance () const |
| Get the tolerance that is used for reaching an orientation goal. This is the tolerance for roll, pitch and yaw, in radians. More... | |
| void | setGoalTolerance (double tolerance) |
| Set the tolerance that is used for reaching the goal. For joint state goals, this will be distance for each joint, in the configuration space (radians or meters depending on joint type). For pose goals this will be the radius of a sphere where the end-effector must reach. This function simply triggers calls to setGoalPositionTolerance(), setGoalOrientationTolerance() and setGoalJointTolerance(). More... | |
| void | setGoalJointTolerance (double tolerance) |
| Set the joint tolerance (for each joint) that is used for reaching the goal when moving to a joint value target. More... | |
| void | setGoalPositionTolerance (double tolerance) |
| Set the position tolerance that is used for reaching the goal when moving to a pose. More... | |
| void | setGoalOrientationTolerance (double tolerance) |
| Set the orientation tolerance that is used for reaching the goal when moving to a pose. More... | |
| void | setWorkspace (double minx, double miny, double minz, double maxx, double maxy, double maxz) |
| Specify the workspace bounding box. The box is specified in the planning frame (i.e. relative to the robot root link start position). This is useful when the planning group contains the root joint of the robot – i.e. when planning motion for the robot relative to the world. More... | |
| void | setStartState (const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotState &start_state) |
| If a different start state should be considered instead of the current state of the robot, this function sets that state. More... | |
| void | setStartState (const moveit::core::RobotState &start_state) |
| If a different start state should be considered instead of the current state of the robot, this function sets that state. More... | |
| void | setStartStateToCurrentState () |
| Set the starting state for planning to be that reported by the robot's joint state publication. More... | |
| void | setSupportSurfaceName (const std::string &name) |
| For pick/place operations, the name of the support surface is used to specify the fact that attached objects are allowed to touch the support surface. More... | |
Setting a joint state target (goal) | |
There are 2 types of goal targets:
Only one or the other is used for planning. Calling any of the set*JointValueTarget() functions sets the current goal target to the JointValueTarget. Calling any of the setPoseTarget(), setOrientationTarget(), setRPYTarget(), setPositionTarget() functions sets the current goal target to the Pose target. | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const std::vector< double > &group_variable_values) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const std::map< std::string, double > &variable_values) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const std::vector< std::string > &variable_names, const std::vector< double > &variable_values) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const moveit::core::RobotState &robot_state) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const std::string &joint_name, const std::vector< double > &values) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const std::string &joint_name, double value) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const sensor_msgs::msg::JointState &state) |
| Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose &eef_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped &eef_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK. More... | |
| bool | setJointValueTarget (const Eigen::Isometry3d &eef_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK. More... | |
| bool | setApproximateJointValueTarget (const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose &eef_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK. More... | |
| bool | setApproximateJointValueTarget (const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped &eef_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK. More... | |
| bool | setApproximateJointValueTarget (const Eigen::Isometry3d &eef_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK. More... | |
| void | setRandomTarget () |
| Set the joint state goal to a random joint configuration. More... | |
| bool | setNamedTarget (const std::string &name) |
| Set the current joint values to be ones previously remembered by rememberJointValues() or, if not found, that are specified in the SRDF under the name name as a group state. More... | |
| void | getJointValueTarget (std::vector< double > &group_variable_values) const |
| Get the current joint state goal in a form compatible to setJointValueTarget() More... | |
| const moveit::core::RobotState & | getJointValueTarget () const |
| Get the currently set joint state goal, replaced by private getTargetRobotState() More... | |
Setting a pose target (goal) | |
Setting a Pose (or Position or Orientation) target disables any previously set JointValueTarget. For groups that have multiple end effectors, a pose can be set for each end effector in the group. End effectors which do not have a pose target set will end up in arbitrary positions. | |
| bool | setPositionTarget (double x, double y, double z, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the goal position of the end-effector end_effector_link to be (x, y, z). More... | |
| bool | setRPYTarget (double roll, double pitch, double yaw, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the goal orientation of the end-effector end_effector_link to be (roll,pitch,yaw) radians. More... | |
| bool | setOrientationTarget (double x, double y, double z, double w, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the goal orientation of the end-effector end_effector_link to be the quaternion (x,y,z,w). More... | |
| bool | setPoseTarget (const Eigen::Isometry3d &end_effector_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the goal pose of the end-effector end_effector_link. More... | |
| bool | setPoseTarget (const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose &target, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the goal pose of the end-effector end_effector_link. More... | |
| bool | setPoseTarget (const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped &target, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set the goal pose of the end-effector end_effector_link. More... | |
| bool | setPoseTargets (const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d &end_effector_pose, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set goal poses for end_effector_link. More... | |
| bool | setPoseTargets (const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::Pose > &target, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set goal poses for end_effector_link. More... | |
| bool | setPoseTargets (const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped > &target, const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Set goal poses for end_effector_link. More... | |
| void | setPoseReferenceFrame (const std::string &pose_reference_frame) |
| Specify which reference frame to assume for poses specified without a reference frame. More... | |
| bool | setEndEffectorLink (const std::string &end_effector_link) |
| Specify the parent link of the end-effector. This end_effector_link will be used in calls to pose target functions when end_effector_link is not explicitly specified. More... | |
| bool | setEndEffector (const std::string &eef_name) |
| Specify the name of the end-effector to use. This is equivalent to setting the EndEffectorLink to the parent link of this end effector. More... | |
| void | clearPoseTarget (const std::string &end_effector_link="") |
| Forget pose(s) specified for end_effector_link. More... | |
| void | clearPoseTargets () |
| Forget any poses specified for all end-effectors. More... | |
| const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & | getPoseTarget (const std::string &end_effector_link="") const |
| const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped > & | getPoseTargets (const std::string &end_effector_link="") const |
| const std::string & | getEndEffectorLink () const |
| Get the current end-effector link. This returns the value set by setEndEffectorLink() (or indirectly by setEndEffector()). If setEndEffectorLink() was not called, this function reports the link name that serves as parent of an end-effector attached to this group. If there are multiple end-effectors, one of them is returned. If no such link is known, the empty string is returned. More... | |
| const std::string & | getEndEffector () const |
| Get the current end-effector name. This returns the value set by setEndEffector() (or indirectly by setEndEffectorLink()). If setEndEffector() was not called, this function reports an end-effector attached to this group. If there are multiple end-effectors, one of them is returned. If no end-effector is known, the empty string is returned. More... | |
| const std::string & | getPoseReferenceFrame () const |
| Get the reference frame set by setPoseReferenceFrame(). By default this is the reference frame of the robot model. More... | |
Planning a path from the start position to the Target (goal) position, and executing that plan. | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | asyncMove () |
| Plan and execute a trajectory that takes the group of joints declared in the constructor to the specified target. This call is not blocking (does not wait for the execution of the trajectory to complete). More... | |
| rclcpp_action::Client< moveit_msgs::action::MoveGroup > & | getMoveGroupClient () const |
| Get the move_group action client used by the MoveGroupInterface. The client can be used for querying the execution state of the trajectory and abort trajectory execution during asynchronous execution. More... | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | move () |
| Plan and execute a trajectory that takes the group of joints declared in the constructor to the specified target. This call is always blocking (waits for the execution of the trajectory to complete) and requires an asynchronous spinner to be started. More... | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | plan (Plan &plan) |
| Compute a motion plan that takes the group declared in the constructor from the current state to the specified target. No execution is performed. The resulting plan is stored in plan. More... | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | asyncExecute (const Plan &plan) |
| Given a plan, execute it without waiting for completion. More... | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | asyncExecute (const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory &trajectory) |
| Given a robot trajectory, execute it without waiting for completion. More... | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | execute (const Plan &plan) |
| Given a plan, execute it while waiting for completion. More... | |
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode | execute (const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory &trajectory) |
| Given a robot trajectory, execute it while waiting for completion. More... | |
| double | computeCartesianPath (const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::Pose > &waypoints, double eef_step, double jump_threshold, moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory &trajectory, bool avoid_collisions=true, moveit_msgs::msg::MoveItErrorCodes *error_code=nullptr) |
| Compute a Cartesian path that follows specified waypoints with a step size of at most eef_step meters between end effector configurations of consecutive points in the result trajectory. The reference frame for the waypoints is that specified by setPoseReferenceFrame(). No more than jump_threshold is allowed as change in distance in the configuration space of the robot (this is to prevent 'jumps' in IK solutions). Collisions are avoided if avoid_collisions is set to true. If collisions cannot be avoided, the function fails. Return a value that is between 0.0 and 1.0 indicating the fraction of the path achieved as described by the waypoints. Return -1.0 in case of error. More... | |
| double | computeCartesianPath (const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::Pose > &waypoints, double eef_step, double jump_threshold, moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory &trajectory, const moveit_msgs::msg::Constraints &path_constraints, bool avoid_collisions=true, moveit_msgs::msg::MoveItErrorCodes *error_code=nullptr) |
| Compute a Cartesian path that follows specified waypoints with a step size of at most eef_step meters between end effector configurations of consecutive points in the result trajectory. The reference frame for the waypoints is that specified by setPoseReferenceFrame(). No more than jump_threshold is allowed as change in distance in the configuration space of the robot (this is to prevent 'jumps' in IK solutions). Kinematic constraints for the path given by path_constraints will be met for every point along the trajectory, if they are not met, a partial solution will be returned. Constraints are checked (collision and kinematic) if avoid_collisions is set to true. If constraints cannot be met, the function fails. Return a value that is between 0.0 and 1.0 indicating the fraction of the path achieved as described by the waypoints. Return -1.0 in case of error. More... | |
| void | stop () |
| Stop any trajectory execution, if one is active. More... | |
| void | allowReplanning (bool flag) |
| Specify whether the robot is allowed to replan if it detects changes in the environment. More... | |
| void | setReplanAttempts (int32_t attempts) |
| Maximum number of replanning attempts. More... | |
| void | setReplanDelay (double delay) |
| Sleep this duration between replanning attempts (in walltime seconds) More... | |
| void | allowLooking (bool flag) |
| Specify whether the robot is allowed to look around before moving if it determines it should (default is false) More... | |
| void | setLookAroundAttempts (int32_t attempts) |
| How often is the system allowed to move the camera to update environment model when looking. More... | |
| void | constructMotionPlanRequest (moveit_msgs::msg::MotionPlanRequest &request) |
| Build the MotionPlanRequest that would be sent to the move_group action with plan() or move() and store it in request. More... | |
High level actions that trigger a sequence of plans and actions. | |
Build a PickupGoal for an object named object and store it in goal_out | |
| bool | attachObject (const std::string &object, const std::string &link="") |
| Pick up an object. More... | |
| bool | attachObject (const std::string &object, const std::string &link, const std::vector< std::string > &touch_links) |
| Given the name of an object in the planning scene, make the object attached to a link of the robot. The set of links the object is allowed to touch without considering that a collision is specified by touch_links. If link is empty, the end-effector link is used. If there is no end-effector, the first link in the group is used. If the object name does not exist an error will be produced in move_group, but the request made by this interface will succeed. More... | |
| bool | detachObject (const std::string &name="") |
| Detach an object. name specifies the name of the object attached to this group, or the name of the link the object is attached to. If there is no name specified, and there is only one attached object, that object is detached. An error is produced if no object to detach is identified. More... | |
Query current robot state | |
| bool | startStateMonitor (double wait=1.0) |
| When reasoning about the current state of a robot, a CurrentStateMonitor instance is automatically constructed. This function allows triggering the construction of that object from the beginning, so that future calls to functions such as getCurrentState() will not take so long and are less likely to fail. More... | |
| std::vector< double > | getCurrentJointValues () const |
| Get the current joint values for the joints planned for by this instance (see getJoints()) More... | |
| moveit::core::RobotStatePtr | getCurrentState (double wait=1) const |
| Get the current state of the robot within the duration specified by wait. More... | |
| geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped | getCurrentPose (const std::string &end_effector_link="") const |
| Get the pose for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed. More... | |
| std::vector< double > | getCurrentRPY (const std::string &end_effector_link="") const |
| Get the roll-pitch-yaw (XYZ) for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed. More... | |
| std::vector< double > | getRandomJointValues () const |
| Get random joint values for the joints planned for by this instance (see getJoints()) More... | |
| geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped | getRandomPose (const std::string &end_effector_link="") const |
| Get a random reachable pose for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed. More... | |
Manage named joint configurations | |
| void | rememberJointValues (const std::string &name) |
| Remember the current joint values (of the robot being monitored) under name. These can be used by setNamedTarget(). These values are remembered locally in the client. Other clients will not have access to them. More... | |
| void | rememberJointValues (const std::string &name, const std::vector< double > &values) |
| Remember the specified joint values under name. These can be used by setNamedTarget(). These values are remembered locally in the client. Other clients will not have access to them. More... | |
| const std::map< std::string, std::vector< double > > & | getRememberedJointValues () const |
| Get the currently remembered map of names to joint values. More... | |
| void | forgetJointValues (const std::string &name) |
| Forget the joint values remembered under name. More... | |
Manage planning constraints | |
| void | setConstraintsDatabase (const std::string &host, unsigned int port) |
| Specify where the database server that holds known constraints resides. More... | |
| std::vector< std::string > | getKnownConstraints () const |
| Get the names of the known constraints as read from the Mongo database, if a connection was achieved. More... | |
| moveit_msgs::msg::Constraints | getPathConstraints () const |
| Get the actual set of constraints in use with this MoveGroupInterface. More... | |
| bool | setPathConstraints (const std::string &constraint) |
| Specify a set of path constraints to use. The constraints are looked up by name from the Mongo database server. This replaces any path constraints set in previous calls to setPathConstraints(). More... | |
| void | setPathConstraints (const moveit_msgs::msg::Constraints &constraint) |
| Specify a set of path constraints to use. This version does not require a database server. This replaces any path constraints set in previous calls to setPathConstraints(). More... | |
| void | clearPathConstraints () |
| Specify that no path constraints are to be used. This removes any path constraints set in previous calls to setPathConstraints(). More... | |
| moveit_msgs::msg::TrajectoryConstraints | getTrajectoryConstraints () const |
| void | setTrajectoryConstraints (const moveit_msgs::msg::TrajectoryConstraints &constraint) |
| void | clearTrajectoryConstraints () |
Static Public Attributes | |
| static const std::string | ROBOT_DESCRIPTION |
| Default ROS parameter name from where to read the robot's URDF. Set to 'robot_description'. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| const moveit::core::RobotState & | getTargetRobotState () const |
Detailed Description
Client class to conveniently use the ROS interfaces provided by the move_group node.
This class includes many default settings to make things easy to use.
Definition at line 80 of file move_group_interface.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ MoveGroupInterface() [1/4]
| moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::MoveGroupInterface | ( | const rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr & | node, |
| const Options & | opt, | ||
| const std::shared_ptr< tf2_ros::Buffer > & | tf_buffer = std::shared_ptr<tf2_ros::Buffer>(), |
||
| const rclcpp::Duration & | wait_for_servers = rclcpp::Duration::from_seconds(-1) |
||
| ) |
Construct a MoveGroupInterface instance call using a specified set of options opt.
- Parameters
-
opt. A MoveGroupInterface::Options structure, if you pass a ros::NodeHandle with a specific callback queue, it has to be of type ros::CallbackQueue (which is the default type of callback queues used in ROS) tf_buffer. Specify a TF2_ROS Buffer instance to use. If not specified, one will be constructed internally wait_for_servers. Timeout for connecting to action servers. -1 time means unlimited waiting.
Definition at line 1407 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ MoveGroupInterface() [2/4]
| moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::MoveGroupInterface | ( | const rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr & | node, |
| const std::string & | group, | ||
| const std::shared_ptr< tf2_ros::Buffer > & | tf_buffer = std::shared_ptr<tf2_ros::Buffer>(), |
||
| const rclcpp::Duration & | wait_for_servers = rclcpp::Duration::from_seconds(-1) |
||
| ) |
Construct a client for the MoveGroup action for a particular group.
- Parameters
-
tf_buffer. Specify a TF2_ROS Buffer instance to use. If not specified, one will be constructed internally wait_for_servers. Timeout for connecting to action servers. -1 time means unlimited waiting.
Definition at line 1397 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ ~MoveGroupInterface()
| moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::~MoveGroupInterface | ( | ) |
Definition at line 1414 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ MoveGroupInterface() [3/4]
|
delete |
This class owns unique resources (e.g. action clients, threads) and its not very meaningful to copy. Pass by references, move it, or simply create multiple instances where required.
◆ MoveGroupInterface() [4/4]
|
noexcept |
Definition at line 1419 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
Member Function Documentation
◆ allowLooking()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::allowLooking | ( | bool | flag | ) |
Specify whether the robot is allowed to look around before moving if it determines it should (default is false)
Definition at line 2228 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ allowReplanning()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::allowReplanning | ( | bool | flag | ) |
Specify whether the robot is allowed to replan if it detects changes in the environment.
Definition at line 2247 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ asyncExecute() [1/2]
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::asyncExecute | ( | const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory & | trajectory | ) |
Given a robot trajectory, execute it without waiting for completion.
Definition at line 1542 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ asyncExecute() [2/2]
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::asyncExecute | ( | const Plan & | plan | ) |
Given a plan, execute it without waiting for completion.
Definition at line 1537 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
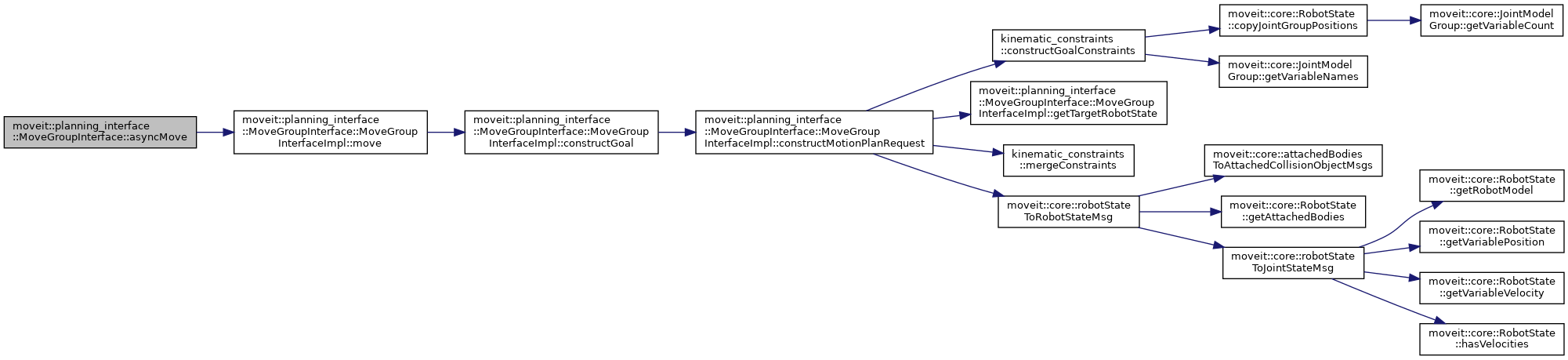
◆ asyncMove()
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::asyncMove | ( | ) |
Plan and execute a trajectory that takes the group of joints declared in the constructor to the specified target. This call is not blocking (does not wait for the execution of the trajectory to complete).
Definition at line 1522 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ attachObject() [1/2]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::attachObject | ( | const std::string & | object, |
| const std::string & | link, | ||
| const std::vector< std::string > & | touch_links | ||
| ) |
Given the name of an object in the planning scene, make the object attached to a link of the robot. The set of links the object is allowed to touch without considering that a collision is specified by touch_links. If link is empty, the end-effector link is used. If there is no end-effector, the first link in the group is used. If the object name does not exist an error will be produced in move_group, but the request made by this interface will succeed.
Definition at line 2361 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ attachObject() [2/2]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::attachObject | ( | const std::string & | object, |
| const std::string & | link = "" |
||
| ) |
Pick up an object.
This applies a number of hard-coded default grasps
Pick up an object given a grasp pose
Pick up an object given possible grasp poses
Pick up an object given a PickupGoal
Use as follows: first create the goal with constructPickupGoal(), then set possible_grasps and any other desired variable in the goal, and finally pass it on to this function
Pick up an object
calls the external moveit_msgs::srv::GraspPlanning service "plan_grasps" to compute possible grasps
Pick up an object calls the external moveit_msgs::srv::GraspPlanning service "plan_grasps" to compute possible grasps
Place an object somewhere safe in the world (a safe location will be detected)
Place an object at one of the specified possible locations
Place an object at one of the specified possible locations
Place an object at one of the specified possible location
Place an object given a PlaceGoal
Use as follows: first create the goal with constructPlaceGoal(), then set place_locations and any other desired variable in the goal, and finally pass it on to this function
Given the name of an object in the planning scene, make the object attached to a link of the robot. If no link name is specified, the end-effector is used. If there is no end-effector, the first link in the group is used. If the object name does not exist an error will be produced in move_group, but the request made by this interface will succeed.
Definition at line 2356 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
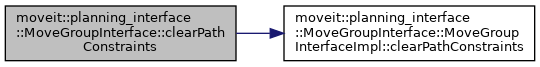
◆ clearPathConstraints()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::clearPathConstraints | ( | ) |
Specify that no path constraints are to be used. This removes any path constraints set in previous calls to setPathConstraints().
Definition at line 2299 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
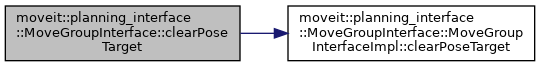
◆ clearPoseTarget()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::clearPoseTarget | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" | ) |
Forget pose(s) specified for end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1868 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
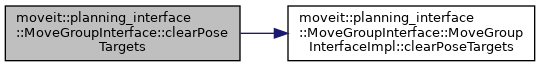
◆ clearPoseTargets()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::clearPoseTargets | ( | ) |
Forget any poses specified for all end-effectors.
Definition at line 1873 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ clearTrajectoryConstraints()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::clearTrajectoryConstraints | ( | ) |
◆ computeCartesianPath() [1/2]
| double moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::computeCartesianPath | ( | const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::Pose > & | waypoints, |
| double | eef_step, | ||
| double | jump_threshold, | ||
| moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory & | trajectory, | ||
| bool | avoid_collisions = true, |
||
| moveit_msgs::msg::MoveItErrorCodes * | error_code = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Compute a Cartesian path that follows specified waypoints with a step size of at most eef_step meters between end effector configurations of consecutive points in the result trajectory. The reference frame for the waypoints is that specified by setPoseReferenceFrame(). No more than jump_threshold is allowed as change in distance in the configuration space of the robot (this is to prevent 'jumps' in IK solutions). Collisions are avoided if avoid_collisions is set to true. If collisions cannot be avoided, the function fails. Return a value that is between 0.0 and 1.0 indicating the fraction of the path achieved as described by the waypoints. Return -1.0 in case of error.
Definition at line 1602 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ computeCartesianPath() [2/2]
| double moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::computeCartesianPath | ( | const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::Pose > & | waypoints, |
| double | eef_step, | ||
| double | jump_threshold, | ||
| moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory & | trajectory, | ||
| const moveit_msgs::msg::Constraints & | path_constraints, | ||
| bool | avoid_collisions = true, |
||
| moveit_msgs::msg::MoveItErrorCodes * | error_code = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Compute a Cartesian path that follows specified waypoints with a step size of at most eef_step meters between end effector configurations of consecutive points in the result trajectory. The reference frame for the waypoints is that specified by setPoseReferenceFrame(). No more than jump_threshold is allowed as change in distance in the configuration space of the robot (this is to prevent 'jumps' in IK solutions). Kinematic constraints for the path given by path_constraints will be met for every point along the trajectory, if they are not met, a partial solution will be returned. Constraints are checked (collision and kinematic) if avoid_collisions is set to true. If constraints cannot be met, the function fails. Return a value that is between 0.0 and 1.0 indicating the fraction of the path achieved as described by the waypoints. Return -1.0 in case of error.
Definition at line 1611 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
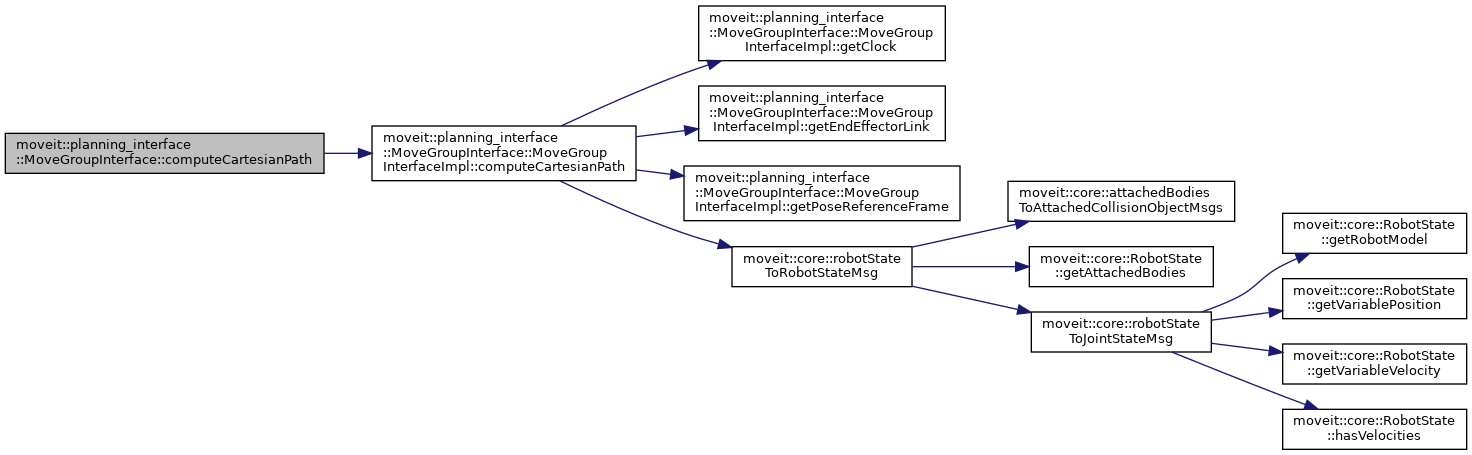
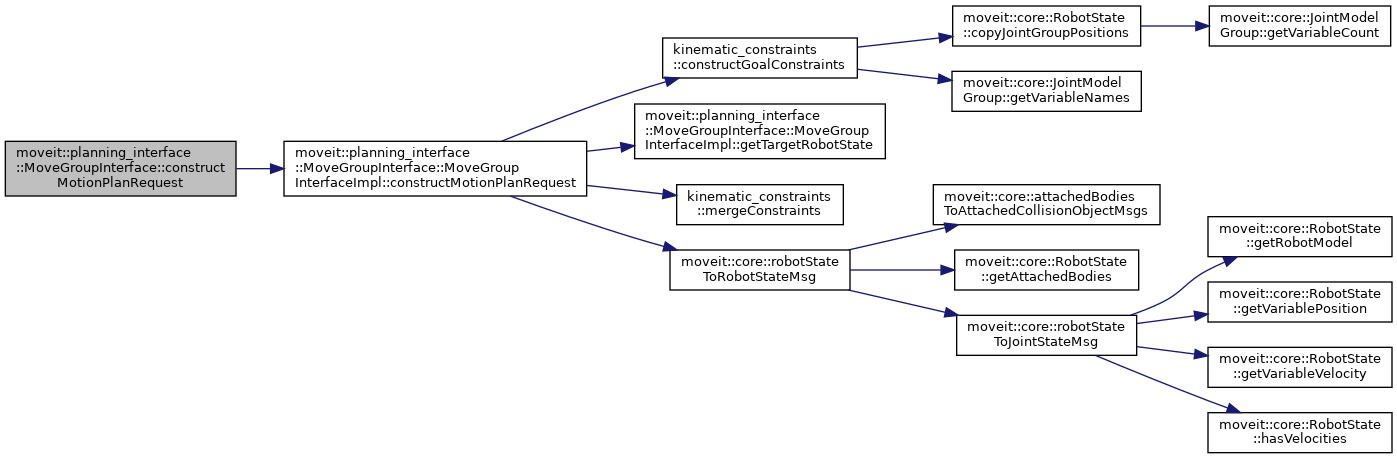
◆ constructMotionPlanRequest()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::constructMotionPlanRequest | ( | moveit_msgs::msg::MotionPlanRequest & | request | ) |
Build the MotionPlanRequest that would be sent to the move_group action with plan() or move() and store it in request.
Definition at line 2372 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ detachObject()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::detachObject | ( | const std::string & | name = "" | ) |
Detach an object. name specifies the name of the object attached to this group, or the name of the link the object is attached to. If there is no name specified, and there is only one attached object, that object is detached. An error is produced if no object to detach is identified.
Definition at line 2367 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ execute() [1/2]
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::execute | ( | const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotTrajectory & | trajectory | ) |
Given a robot trajectory, execute it while waiting for completion.
Definition at line 1552 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ execute() [2/2]
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::execute | ( | const Plan & | plan | ) |
Given a plan, execute it while waiting for completion.
Definition at line 1547 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ forgetJointValues()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::forgetJointValues | ( | const std::string & | name | ) |
Forget the joint values remembered under name.
Definition at line 2223 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getActiveJoints()
| const std::vector< std::string > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getActiveJoints | ( | ) | const |
Get only the active (actuated) joints this instance operates on.
Definition at line 2196 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getCurrentJointValues()
| std::vector< double > moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getCurrentJointValues | ( | ) | const |
Get the current joint values for the joints planned for by this instance (see getJoints())
Definition at line 2104 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ getCurrentPose()
| geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getCurrentPose | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" | ) | const |
Get the pose for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed.
Definition at line 2145 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getCurrentRPY()
| std::vector< double > moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getCurrentRPY | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" | ) | const |
Get the roll-pitch-yaw (XYZ) for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed.
Definition at line 2169 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getCurrentState()
| moveit::core::RobotStatePtr moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getCurrentState | ( | double | wait = 1 | ) | const |
Get the current state of the robot within the duration specified by wait.
Definition at line 2211 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getDefaultPlannerId()
| std::string moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getDefaultPlannerId | ( | const std::string & | group = "" | ) | const |
Get the default planner of the current planning pipeline for the given group (or the pipeline's default)
Definition at line 1492 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ getDefaultPlanningPipelineId()
| std::string moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getDefaultPlanningPipelineId | ( | ) | const |
◆ getEndEffector()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getEndEffector | ( | ) | const |
Get the current end-effector name. This returns the value set by setEndEffector() (or indirectly by setEndEffectorLink()). If setEndEffector() was not called, this function reports an end-effector attached to this group. If there are multiple end-effectors, one of them is returned. If no end-effector is known, the empty string is returned.
Definition at line 1846 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ getEndEffectorLink()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getEndEffectorLink | ( | ) | const |
Get the current end-effector link. This returns the value set by setEndEffectorLink() (or indirectly by setEndEffector()). If setEndEffectorLink() was not called, this function reports the link name that serves as parent of an end-effector attached to this group. If there are multiple end-effectors, one of them is returned. If no such link is known, the empty string is returned.
Definition at line 1841 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getGoalJointTolerance()
| double moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getGoalJointTolerance | ( | ) | const |
Get the tolerance that is used for reaching a joint goal. This is distance for each joint in configuration space.
Definition at line 2057 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getGoalOrientationTolerance()
| double moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getGoalOrientationTolerance | ( | ) | const |
Get the tolerance that is used for reaching an orientation goal. This is the tolerance for roll, pitch and yaw, in radians.
Definition at line 2067 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getGoalPositionTolerance()
| double moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getGoalPositionTolerance | ( | ) | const |
Get the tolerance that is used for reaching a position goal. This is be the radius of a sphere where the end-effector must reach.
Definition at line 2062 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getInterfaceDescription()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getInterfaceDescription | ( | moveit_msgs::msg::PlannerInterfaceDescription & | desc | ) | const |
Get the description of the default planning plugin loaded by the action server.
Definition at line 1455 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getInterfaceDescriptions()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getInterfaceDescriptions | ( | std::vector< moveit_msgs::msg::PlannerInterfaceDescription > & | desc | ) | const |
Get the descriptions of all planning plugins loaded by the action server.
Definition at line 1460 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getJointModelGroupNames()
| const std::vector< std::string > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getJointModelGroupNames | ( | ) | const |
Get the available planning group names.
Definition at line 2351 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getJointNames()
| const std::vector< std::string > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getJointNames | ( | ) | const |
Get vector of names of joints available in move group.
Definition at line 1655 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getJoints()
| const std::vector< std::string > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getJoints | ( | ) | const |
Get all the joints this instance operates on (including fixed joints)
Definition at line 2201 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getJointValueTarget() [1/2]
| const moveit::core::RobotState & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getJointValueTarget | ( | ) | const |
Get the currently set joint state goal, replaced by private getTargetRobotState()
Definition at line 1831 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getJointValueTarget() [2/2]
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getJointValueTarget | ( | std::vector< double > & | group_variable_values | ) | const |
Get the current joint state goal in a form compatible to setJointValueTarget()
Definition at line 1704 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getKnownConstraints()
| std::vector< std::string > moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getKnownConstraints | ( | ) | const |
Get the names of the known constraints as read from the Mongo database, if a connection was achieved.
Definition at line 2279 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getLinkNames()
| const std::vector< std::string > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getLinkNames | ( | ) | const |
Get vector of names of links available in move group.
Definition at line 1660 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getMoveGroupClient()
| rclcpp_action::Client< moveit_msgs::action::MoveGroup > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getMoveGroupClient | ( | ) | const |
Get the move_group action client used by the MoveGroupInterface. The client can be used for querying the execution state of the trajectory and abort trajectory execution during asynchronous execution.
Definition at line 1527 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getName()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getName | ( | ) | const |
Get the name of the group this instance operates on.
Definition at line 1438 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ getNamedTargets()
| const std::vector< std::string > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getNamedTargets | ( | ) | const |
Get the names of the named robot states available as targets, both either remembered states or default states from srdf.
Definition at line 1443 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getNamedTargetValues()
| std::map< std::string, double > moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getNamedTargetValues | ( | const std::string & | name | ) | const |
Get the joint angles for targets specified by name.
Definition at line 1665 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getNodeHandle()
| rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getNodeHandle | ( | ) |
Get the ROS node handle of this instance operates on.
◆ getPathConstraints()
| moveit_msgs::msg::Constraints moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPathConstraints | ( | ) | const |
Get the actual set of constraints in use with this MoveGroupInterface.
- Returns
- A copy of the current path constraints set for this interface
Definition at line 2284 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPlannerId()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPlannerId | ( | ) | const |
Get the current planner_id.
Definition at line 1502 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPlannerParams()
| std::map< std::string, std::string > moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPlannerParams | ( | const std::string & | planner_id, |
| const std::string & | group = "" |
||
| ) | const |
Get the planner parameters for given group and planner_id.
Definition at line 1465 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPlanningFrame()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPlanningFrame | ( | ) | const |
Get the name of the frame in which the robot is planning.
Definition at line 2346 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPlanningPipelineId()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPlanningPipelineId | ( | ) | const |
Get the current planning_pipeline_id.
Definition at line 1487 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPlanningTime()
| double moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPlanningTime | ( | ) | const |
Get the number of seconds set by setPlanningTime()
Get time allowed to planner to solve problem before aborting.
Definition at line 2336 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPoseReferenceFrame()
| const std::string & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPoseReferenceFrame | ( | ) | const |
Get the reference frame set by setPoseReferenceFrame(). By default this is the reference frame of the robot model.
Definition at line 2052 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPoseTarget()
| const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPoseTarget | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" | ) | const |
Get the currently set pose goal for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed. If multiple targets are set for end_effector_link this will return the first one. If no pose target is set for this end_effector_link then an empty pose will be returned (check for orientation.xyzw == 0).
Definition at line 1947 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getPoseTargets()
| const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped > & moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getPoseTargets | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" | ) | const |
Get the currently set pose goal for the end-effector end_effector_link. The pose goal can consist of multiple poses, if corresponding setPoseTarget() calls were made. Otherwise, only one pose is returned in the vector. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed
Definition at line 1953 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getRandomJointValues()
| std::vector< double > moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getRandomJointValues | ( | ) | const |
Get random joint values for the joints planned for by this instance (see getJoints())
Definition at line 2113 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getRandomPose()
| geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getRandomPose | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" | ) | const |
Get a random reachable pose for the end-effector end_effector_link. If end_effector_link is empty (the default value) then the end-effector reported by getEndEffectorLink() is assumed.
Definition at line 2120 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getRememberedJointValues()
|
inline |
Get the currently remembered map of names to joint values.
Definition at line 963 of file move_group_interface.h.
◆ getRobotModel()
| moveit::core::RobotModelConstPtr moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getRobotModel | ( | ) | const |
Get the RobotModel object.
Definition at line 1450 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getTargetRobotState()
|
protected |
return the full RobotState of the joint-space target, only for internal use
Definition at line 1836 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ getTrajectoryConstraints()
| moveit_msgs::msg::TrajectoryConstraints moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getTrajectoryConstraints | ( | ) | const |
◆ getVariableCount()
| unsigned int moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::getVariableCount | ( | ) | const |
Get the number of variables used to describe the state of this group. This is larger or equal to the number of DOF.
Definition at line 2206 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ move()
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::move | ( | ) |
Plan and execute a trajectory that takes the group of joints declared in the constructor to the specified target. This call is always blocking (waits for the execution of the trajectory to complete) and requires an asynchronous spinner to be started.
Definition at line 1532 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ MOVEIT_STRUCT_FORWARD()
| moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::MOVEIT_STRUCT_FORWARD | ( | Plan | ) |
◆ operator=() [1/2]
|
delete |
◆ operator=() [2/2]
|
noexcept |
Definition at line 1425 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ plan()
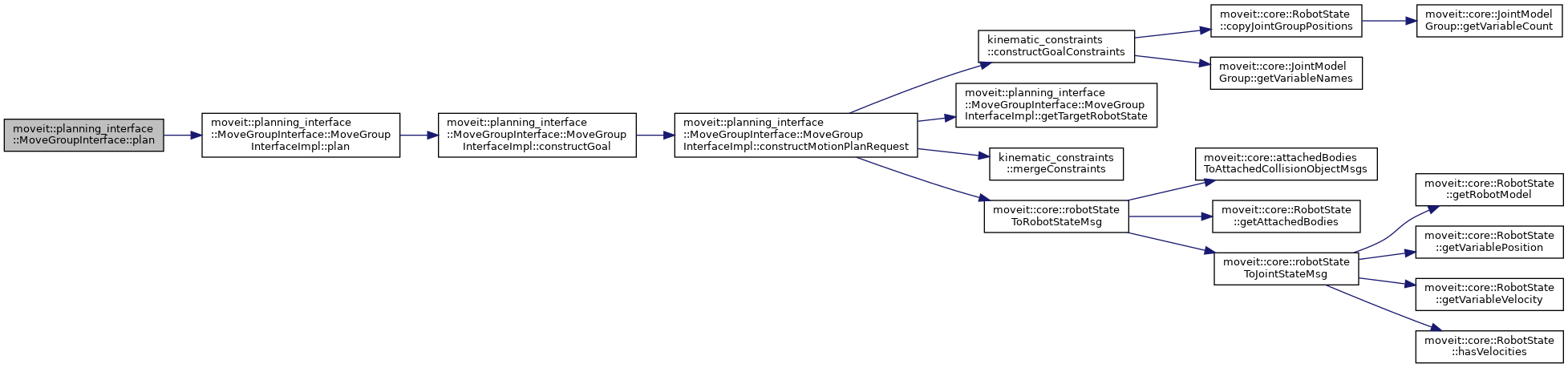
| moveit::core::MoveItErrorCode moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::plan | ( | Plan & | plan | ) |
Compute a motion plan that takes the group declared in the constructor from the current state to the specified target. No execution is performed. The resulting plan is stored in plan.
Definition at line 1557 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ rememberJointValues() [1/2]
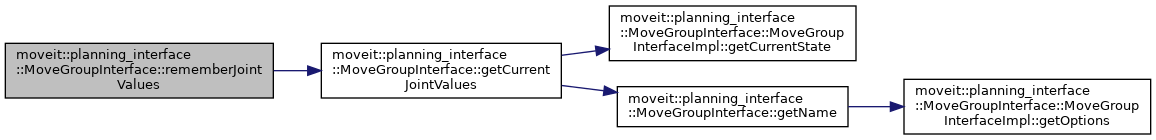
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::rememberJointValues | ( | const std::string & | name | ) |
Remember the current joint values (of the robot being monitored) under name. These can be used by setNamedTarget(). These values are remembered locally in the client. Other clients will not have access to them.
Definition at line 2094 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ rememberJointValues() [2/2]
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::rememberJointValues | ( | const std::string & | name, |
| const std::vector< double > & | values | ||
| ) |
Remember the specified joint values under name. These can be used by setNamedTarget(). These values are remembered locally in the client. Other clients will not have access to them.
Definition at line 2218 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
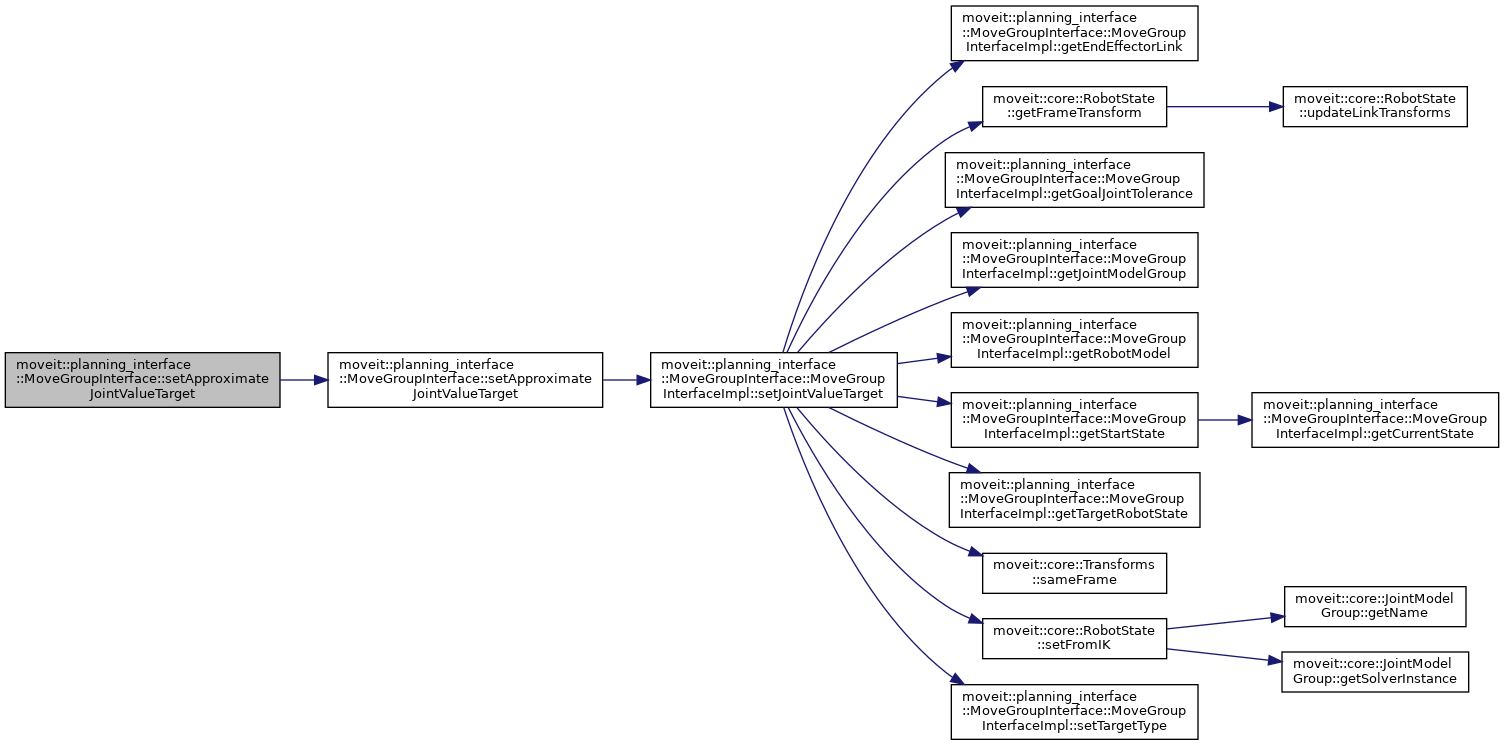
◆ setApproximateJointValueTarget() [1/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setApproximateJointValueTarget | ( | const Eigen::Isometry3d & | eef_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK.
This is different from setPoseTarget() in that a single IK state (aka JointValueTarget) is computed using IK, and the resulting JointValueTarget is used as the target for planning.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If IK fails to find a solution then an approximation is used.
Definition at line 1824 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setApproximateJointValueTarget() [2/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setApproximateJointValueTarget | ( | const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose & | eef_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK.
This is different from setPoseTarget() in that a single IK state (aka JointValueTarget) is computed using IK, and the resulting JointValueTarget is used as the target for planning.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If IK fails to find a solution then an approximation is used.
Definition at line 1812 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
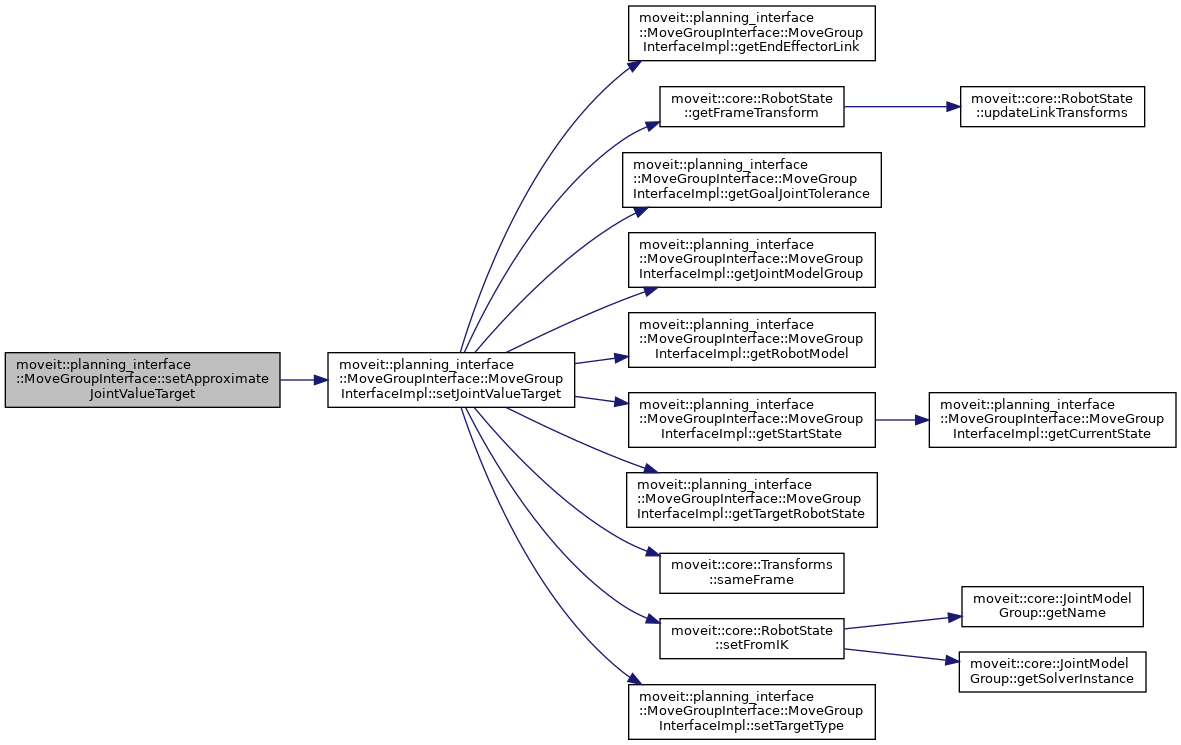
◆ setApproximateJointValueTarget() [3/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setApproximateJointValueTarget | ( | const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & | eef_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK.
This is different from setPoseTarget() in that a single IK state (aka JointValueTarget) is computed using IK, and the resulting JointValueTarget is used as the target for planning.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If IK fails to find a solution then an approximation is used.
Definition at line 1818 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
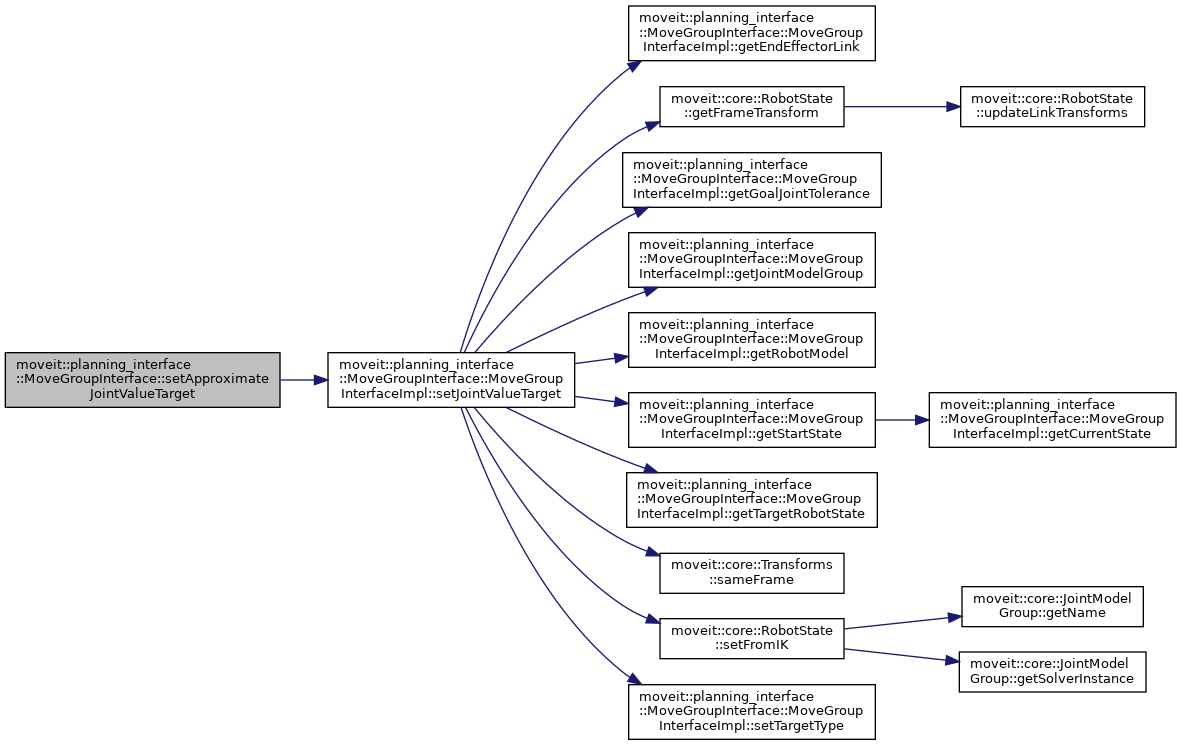
◆ setConstraintsDatabase()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setConstraintsDatabase | ( | const std::string & | host, |
| unsigned int | port | ||
| ) |
Specify where the database server that holds known constraints resides.
Definition at line 2319 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setEndEffector()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setEndEffector | ( | const std::string & | eef_name | ) |
Specify the name of the end-effector to use. This is equivalent to setting the EndEffectorLink to the parent link of this end effector.
Definition at line 1860 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setEndEffectorLink()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setEndEffectorLink | ( | const std::string & | end_effector_link | ) |
Specify the parent link of the end-effector. This end_effector_link will be used in calls to pose target functions when end_effector_link is not explicitly specified.
Definition at line 1851 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ setGoalJointTolerance()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setGoalJointTolerance | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Set the joint tolerance (for each joint) that is used for reaching the goal when moving to a joint value target.
Definition at line 2079 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setGoalOrientationTolerance()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setGoalOrientationTolerance | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Set the orientation tolerance that is used for reaching the goal when moving to a pose.
Definition at line 2089 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setGoalPositionTolerance()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setGoalPositionTolerance | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Set the position tolerance that is used for reaching the goal when moving to a pose.
Definition at line 2084 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setGoalTolerance()
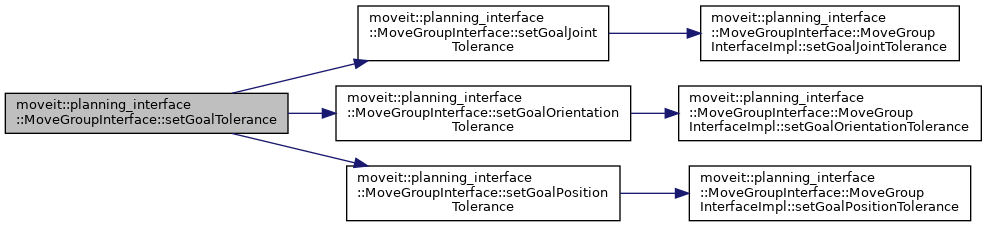
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setGoalTolerance | ( | double | tolerance | ) |
Set the tolerance that is used for reaching the goal. For joint state goals, this will be distance for each joint, in the configuration space (radians or meters depending on joint type). For pose goals this will be the radius of a sphere where the end-effector must reach. This function simply triggers calls to setGoalPositionTolerance(), setGoalOrientationTolerance() and setGoalJointTolerance().
Definition at line 2072 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [1/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const Eigen::Isometry3d & | eef_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK.
This is different from setPoseTarget() in that a single IK state (aka JointValueTarget) is computed using IK, and the resulting JointValueTarget is used as the target for planning.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If IK fails to find a solution then false is returned BUT THE PARTIAL RESULT OF IK IS STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1806 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [2/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose & | eef_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK.
This is different from setPoseTarget() in that a single IK state (aka JointValueTarget) is computed using IK, and the resulting JointValueTarget is used as the target for planning.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If IK fails to find a solution then false is returned BUT THE PARTIAL RESULT OF IK IS STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1794 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [3/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & | eef_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the joint state goal for a particular joint by computing IK.
This is different from setPoseTarget() in that a single IK state (aka JointValueTarget) is computed using IK, and the resulting JointValueTarget is used as the target for planning.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If IK fails to find a solution then false is returned BUT THE PARTIAL RESULT OF IK IS STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1800 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [4/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const moveit::core::RobotState & | robot_state | ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
The target for all joints in the group are set to the value in robot_state.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1761 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [5/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const sensor_msgs::msg::JointState & | state | ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
state is used to set the target joint state values. Values not specified in state remain unchanged.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1789 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [6/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const std::map< std::string, double > & | variable_values | ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
variable_values is a map of joint variable names to values. Joints in the group are used to set the JointValueTarget. Joints in the model but not in the group are ignored. An exception is thrown if a joint name is not found in the model. Joint variables in the group that are missing from variable_values remain unchanged (to reset all target variables to their current values in the robot use setJointValueTarget(getCurrentJointValues())).
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1724 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [7/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const std::string & | joint_name, |
| const std::vector< double > & | values | ||
| ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
values MUST have one value for each variable in joint joint_name. values are set as the target for this joint. Other joint targets remain unchanged.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1774 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setJointValueTarget() [8/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const std::string & | joint_name, |
| double | value | ||
| ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
Joint joint_name must be a 1-DOF joint. value is set as the target for this joint. Other joint targets remain unchanged.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1768 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
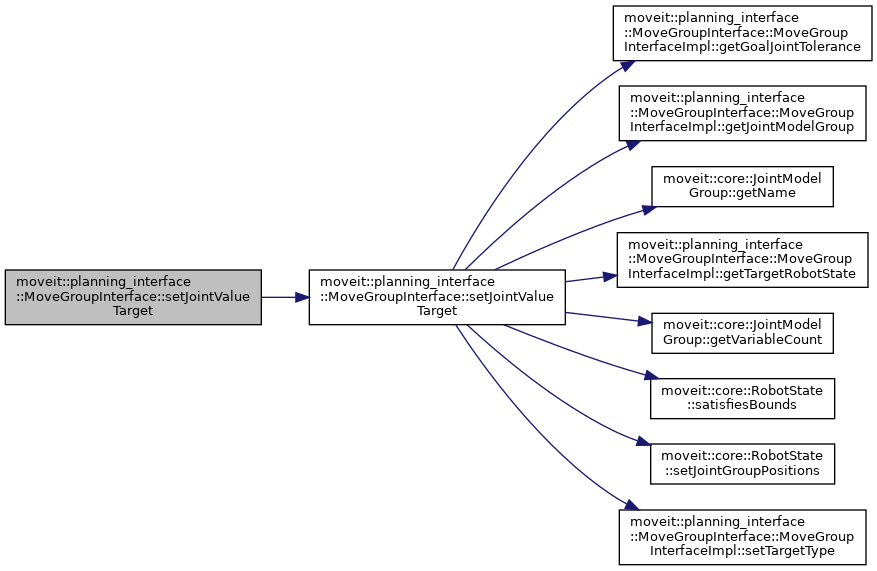
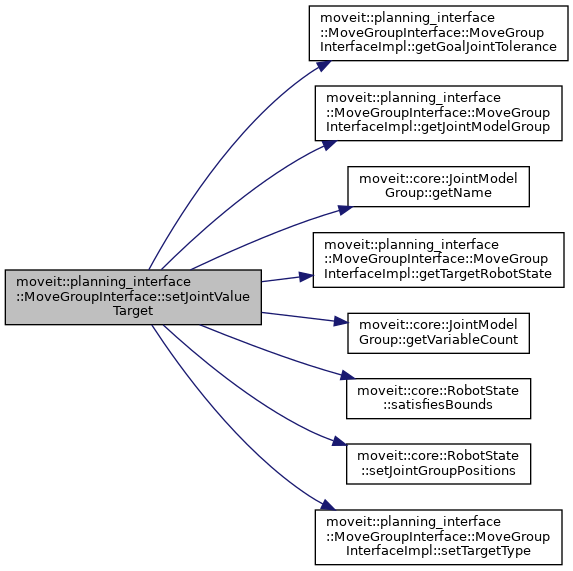
◆ setJointValueTarget() [9/10]
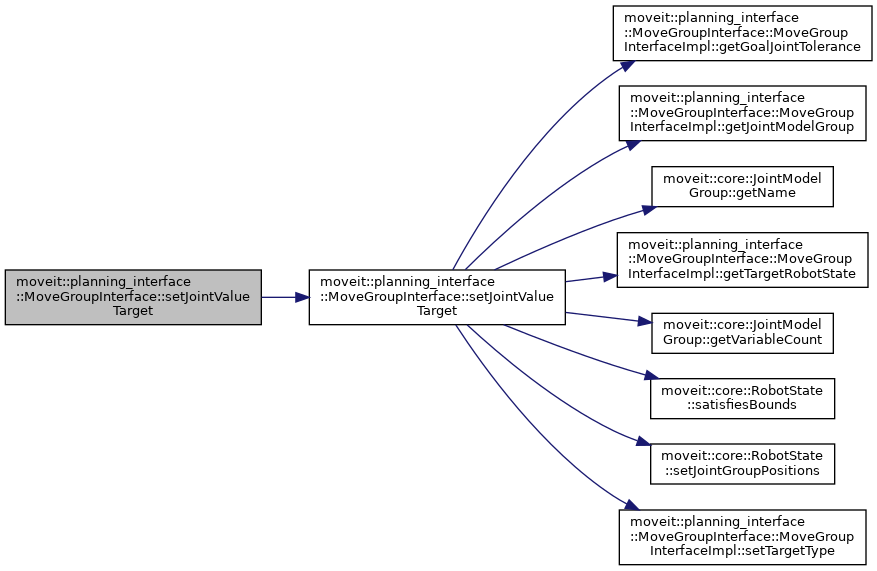
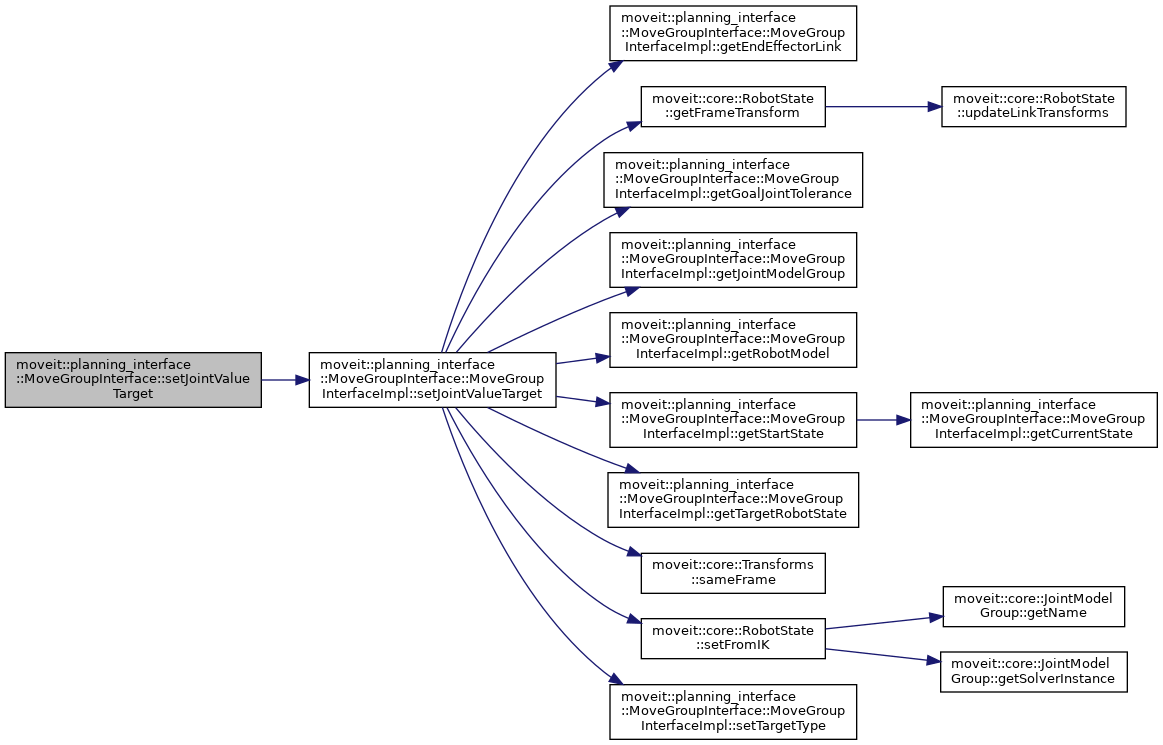
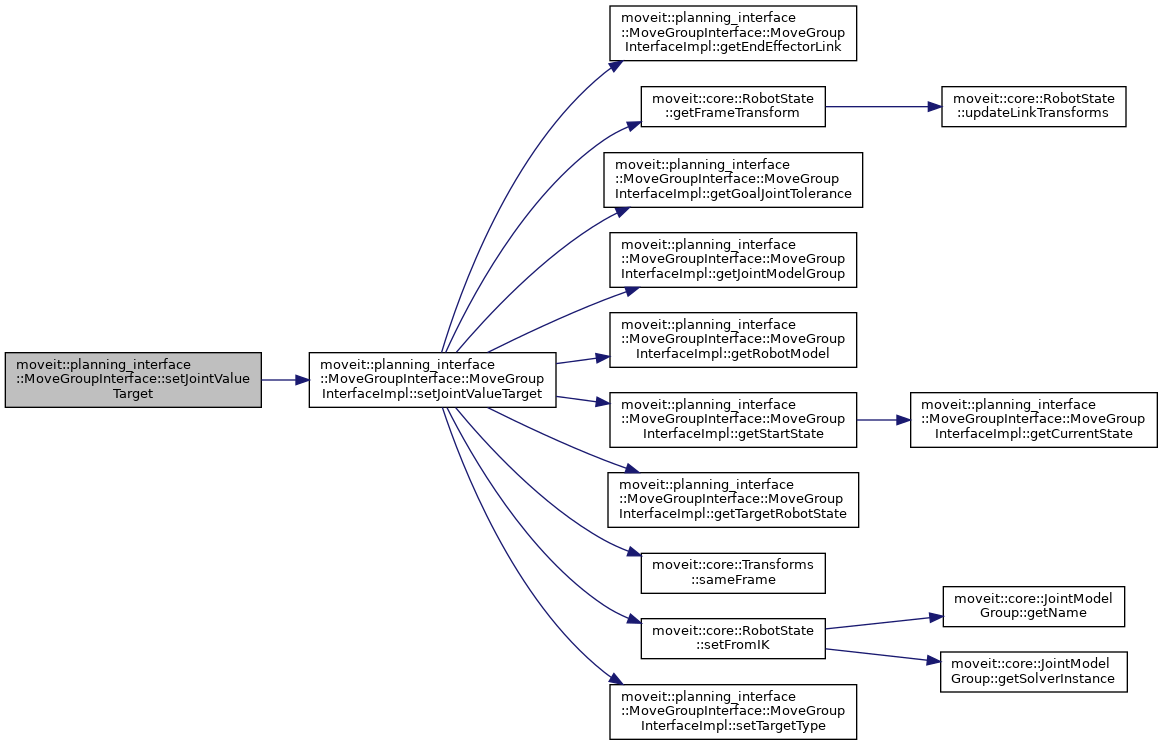
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const std::vector< double > & | group_variable_values | ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
group_variable_values MUST exactly match the variable order as returned by getJointValueTarget(std::vector<double>&).
This always sets all of the group's joint values.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1709 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
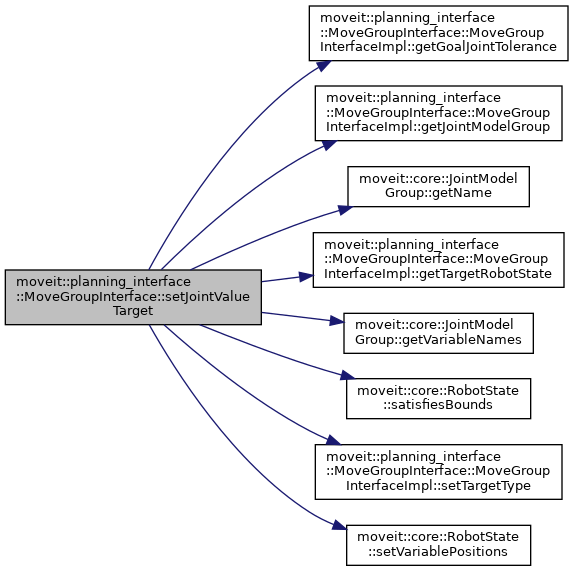
◆ setJointValueTarget() [10/10]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setJointValueTarget | ( | const std::vector< std::string > & | variable_names, |
| const std::vector< double > & | variable_values | ||
| ) |
Set the JointValueTarget and use it for future planning requests.
variable_names are variable joint names and variable_values are variable joint positions. Joints in the group are used to set the JointValueTarget. Joints in the model but not in the group are ignored. An exception is thrown if a joint name is not found in the model. Joint variables in the group that are missing from variable_names remain unchanged (to reset all target variables to their current values in the robot use setJointValueTarget(getCurrentJointValues())).
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
If these values are out of bounds then false is returned BUT THE VALUES ARE STILL SET AS THE GOAL.
Definition at line 1742 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setLookAroundAttempts()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setLookAroundAttempts | ( | int32_t | attempts | ) |
How often is the system allowed to move the camera to update environment model when looking.
Definition at line 2234 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setMaxAccelerationScalingFactor()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setMaxAccelerationScalingFactor | ( | double | max_acceleration_scaling_factor | ) |
Set a scaling factor for optionally reducing the maximum joint acceleration. Allowed values are in (0,1]. The maximum joint acceleration specified in the robot model is multiplied by the factor. If the value is 0, it is set to the default value, which is defined in joint_limits.yaml of the moveit_config. If the value is greater than 1, it is set to 1.0.
Definition at line 1517 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ setMaxVelocityScalingFactor()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setMaxVelocityScalingFactor | ( | double | max_velocity_scaling_factor | ) |
Set a scaling factor for optionally reducing the maximum joint velocity. Allowed values are in (0,1]. The maximum joint velocity specified in the robot model is multiplied by the factor. If the value is 0, it is set to the default value, which is defined in joint_limits.yaml of the moveit_config. If the value is greater than 1, it is set to 1.0.
Definition at line 1512 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ setNamedTarget()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setNamedTarget | ( | const std::string & | name | ) |
Set the current joint values to be ones previously remembered by rememberJointValues() or, if not found, that are specified in the SRDF under the name name as a group state.
Definition at line 1685 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setNumPlanningAttempts()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setNumPlanningAttempts | ( | unsigned int | num_planning_attempts | ) |
Set the number of times the motion plan is to be computed from scratch before the shortest solution is returned. The default value is 1.
Definition at line 1507 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setOrientationTarget()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setOrientationTarget | ( | double | x, |
| double | y, | ||
| double | z, | ||
| double | w, | ||
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the goal orientation of the end-effector end_effector_link to be the quaternion (x,y,z,w).
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 2021 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPathConstraints() [1/2]
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPathConstraints | ( | const moveit_msgs::msg::Constraints & | constraint | ) |
Specify a set of path constraints to use. This version does not require a database server. This replaces any path constraints set in previous calls to setPathConstraints().
Definition at line 2294 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPathConstraints() [2/2]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPathConstraints | ( | const std::string & | constraint | ) |
Specify a set of path constraints to use. The constraints are looked up by name from the Mongo database server. This replaces any path constraints set in previous calls to setPathConstraints().
Definition at line 2289 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPlannerId()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPlannerId | ( | const std::string & | planner_id | ) |
Specify a planner to be used for further planning.
Definition at line 1497 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPlannerParams()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPlannerParams | ( | const std::string & | planner_id, |
| const std::string & | group, | ||
| const std::map< std::string, std::string > & | params, | ||
| bool | bReplace = false |
||
| ) |
Set the planner parameters for given group and planner_id.
Definition at line 1471 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPlanningPipelineId()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPlanningPipelineId | ( | const std::string & | pipeline_id | ) |
Specify a planning pipeline to be used for further planning.
Definition at line 1482 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPlanningTime()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPlanningTime | ( | double | seconds | ) |
Specify the maximum amount of time to use when planning.
Set time allowed to planner to solve problem before aborting.
Definition at line 2330 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPoseReferenceFrame()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseReferenceFrame | ( | const std::string & | pose_reference_frame | ) |
Specify which reference frame to assume for poses specified without a reference frame.
Definition at line 2047 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPoseTarget() [1/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseTarget | ( | const Eigen::Isometry3d & | end_effector_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the goal pose of the end-effector end_effector_link.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
This new pose target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1878 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPoseTarget() [2/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseTarget | ( | const geometry_msgs::msg::Pose & | target, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the goal pose of the end-effector end_effector_link.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1887 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPoseTarget() [3/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseTarget | ( | const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & | target, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the goal pose of the end-effector end_effector_link.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1896 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPoseTargets() [1/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseTargets | ( | const EigenSTL::vector_Isometry3d & | end_effector_pose, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set goal poses for end_effector_link.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
When planning, the planner will find a path to one (arbitrarily chosen) pose from the list. If this group contains multiple end effectors then all end effectors in the group should have the same number of pose targets. If planning is successful then the result of the plan will place all end effectors at a pose from the same index in the list. (In other words, if one end effector ends up at the 3rd pose in the list then all end effectors in the group will end up at the 3rd pose in their respective lists. End effectors which do not matter (i.e. can end up in any position) can have their pose targets disabled by calling clearPoseTarget() for that end_effector_link.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target(s) for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1903 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPoseTargets() [2/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseTargets | ( | const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::Pose > & | target, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set goal poses for end_effector_link.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
When planning, the planner will find a path to one (arbitrarily chosen) pose from the list. If this group contains multiple end effectors then all end effectors in the group should have the same number of pose targets. If planning is successful then the result of the plan will place all end effectors at a pose from the same index in the list. (In other words, if one end effector ends up at the 3rd pose in the list then all end effectors in the group will end up at the 3rd pose in their respective lists. End effectors which do not matter (i.e. can end up in any position) can have their pose targets disabled by calling clearPoseTarget() for that end_effector_link.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target(s) for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1917 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
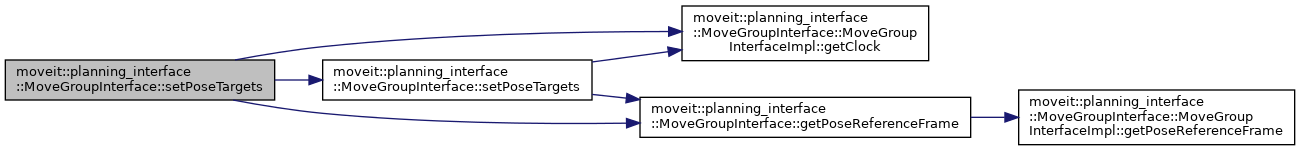
◆ setPoseTargets() [3/3]
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPoseTargets | ( | const std::vector< geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped > & | target, |
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set goal poses for end_effector_link.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
When planning, the planner will find a path to one (arbitrarily chosen) pose from the list. If this group contains multiple end effectors then all end effectors in the group should have the same number of pose targets. If planning is successful then the result of the plan will place all end effectors at a pose from the same index in the list. (In other words, if one end effector ends up at the 3rd pose in the list then all end effectors in the group will end up at the 3rd pose in their respective lists. End effectors which do not matter (i.e. can end up in any position) can have their pose targets disabled by calling clearPoseTarget() for that end_effector_link.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target(s) for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1932 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setPositionTarget()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setPositionTarget | ( | double | x, |
| double | y, | ||
| double | z, | ||
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the goal position of the end-effector end_effector_link to be (x, y, z).
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
This new position target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1973 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setRandomTarget()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setRandomTarget | ( | ) |
Set the joint state goal to a random joint configuration.
After this call, the JointValueTarget is used instead of any previously set Position, Orientation, or Pose targets.
Definition at line 1649 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setReplanAttempts()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setReplanAttempts | ( | int32_t | attempts | ) |
Maximum number of replanning attempts.
Definition at line 2253 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setReplanDelay()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setReplanDelay | ( | double | delay | ) |
Sleep this duration between replanning attempts (in walltime seconds)
Definition at line 2266 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setRPYTarget()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setRPYTarget | ( | double | roll, |
| double | pitch, | ||
| double | yaw, | ||
| const std::string & | end_effector_link = "" |
||
| ) |
Set the goal orientation of the end-effector end_effector_link to be (roll,pitch,yaw) radians.
If end_effector_link is empty then getEndEffectorLink() is used.
This new orientation target replaces any pre-existing JointValueTarget or pre-existing Position, Orientation, or Pose target for this end_effector_link.
Definition at line 1998 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
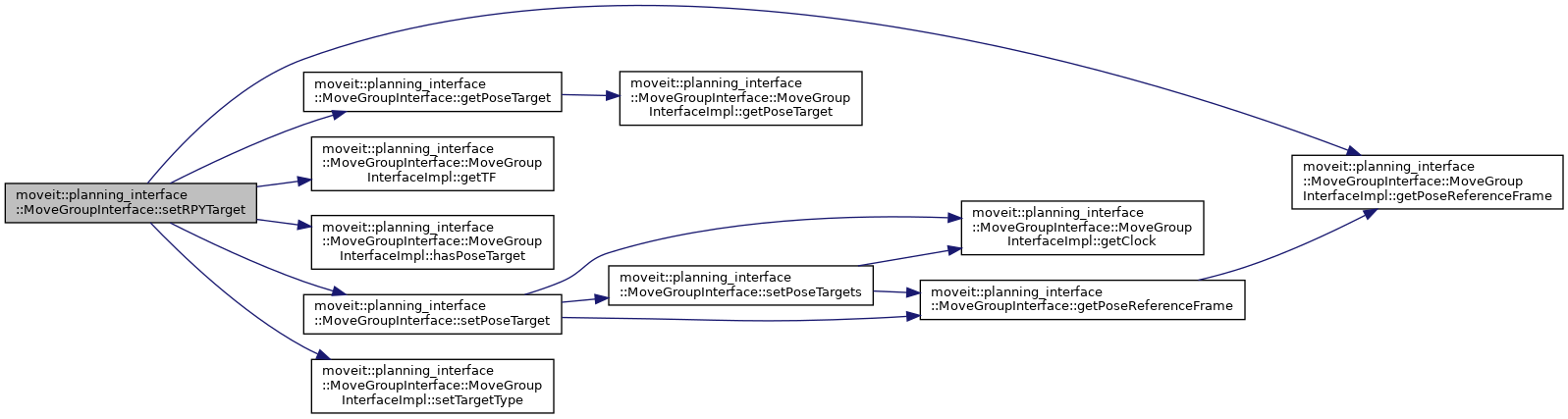
◆ setStartState() [1/2]
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setStartState | ( | const moveit::core::RobotState & | start_state | ) |
If a different start state should be considered instead of the current state of the robot, this function sets that state.
Definition at line 1639 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setStartState() [2/2]
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setStartState | ( | const moveit_msgs::msg::RobotState & | start_state | ) |
If a different start state should be considered instead of the current state of the robot, this function sets that state.
Definition at line 1634 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setStartStateToCurrentState()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setStartStateToCurrentState | ( | ) |
Set the starting state for planning to be that reported by the robot's joint state publication.
Definition at line 1644 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setSupportSurfaceName()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setSupportSurfaceName | ( | const std::string & | name | ) |
For pick/place operations, the name of the support surface is used to specify the fact that attached objects are allowed to touch the support surface.
Definition at line 2341 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ setTrajectoryConstraints()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setTrajectoryConstraints | ( | const moveit_msgs::msg::TrajectoryConstraints & | constraint | ) |
◆ setWorkspace()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::setWorkspace | ( | double | minx, |
| double | miny, | ||
| double | minz, | ||
| double | maxx, | ||
| double | maxy, | ||
| double | maxz | ||
| ) |
Specify the workspace bounding box. The box is specified in the planning frame (i.e. relative to the robot root link start position). This is useful when the planning group contains the root joint of the robot – i.e. when planning motion for the robot relative to the world.
Definition at line 2324 of file move_group_interface.cpp.

◆ startStateMonitor()
| bool moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::startStateMonitor | ( | double | wait = 1.0 | ) |
When reasoning about the current state of a robot, a CurrentStateMonitor instance is automatically constructed. This function allows triggering the construction of that object from the beginning, so that future calls to functions such as getCurrentState() will not take so long and are less likely to fail.
Definition at line 2099 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
◆ stop()
| void moveit::planning_interface::MoveGroupInterface::stop | ( | ) |
Stop any trajectory execution, if one is active.
Definition at line 1629 of file move_group_interface.cpp.
Member Data Documentation
◆ ROBOT_DESCRIPTION
|
static |
Default ROS parameter name from where to read the robot's URDF. Set to 'robot_description'.
Definition at line 84 of file move_group_interface.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- moveit_ros/planning_interface/move_group_interface/include/moveit/move_group_interface/move_group_interface.h
- moveit_ros/planning_interface/move_group_interface/src/move_group_interface.cpp